513.找树左下角的值
题目:513. 找树左下角的值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树的 根节点
root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
输入: root = [2,1,3] 输出: 1示例 2:
输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7] 输出: 7
递归法
前中后序都可以,因为没有中的处理逻辑。
回溯的思想体现在depth,要在递归语句前++,语句后--,其实就是回退的操作,去遍历右子树。
本题理解,找到最后一行的左节点就行,深度最大。
class Solution {
public:int maxdepth=INT_MIN;int result;void trversal(TreeNode*root,int depth){if(root->right==NULL&&root->left==NULL)//找到叶子节点,查看是否是最大深度的{if(depth>maxdepth){maxdepth=depth;result=root->val;}return;}if(root->left){depth++;trversal(root->left,depth);depth--;}if(root->right){depth++;trversal(root->right,depth);depth--;}return;}int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {trversal(root,0);return result;}
};迭代法
使用层序遍历比较简单。。
class Solution {
public:int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {queue<TreeNode*>que;int result=0;if(root)que.push(root);while(!que.empty()){int size=que.size();for(int i=0;i<size;i++){TreeNode*node=que.front();que.pop();//其实没弹出一个结点,就弹进该节点的左右孩子if(i==0)result=node->val;//记录最后一行第一个元素if (node->left) que.push(node->left);if (node->right) que.push(node->right);}}return result;}
};112.路径总和
题目:112. 路径总和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
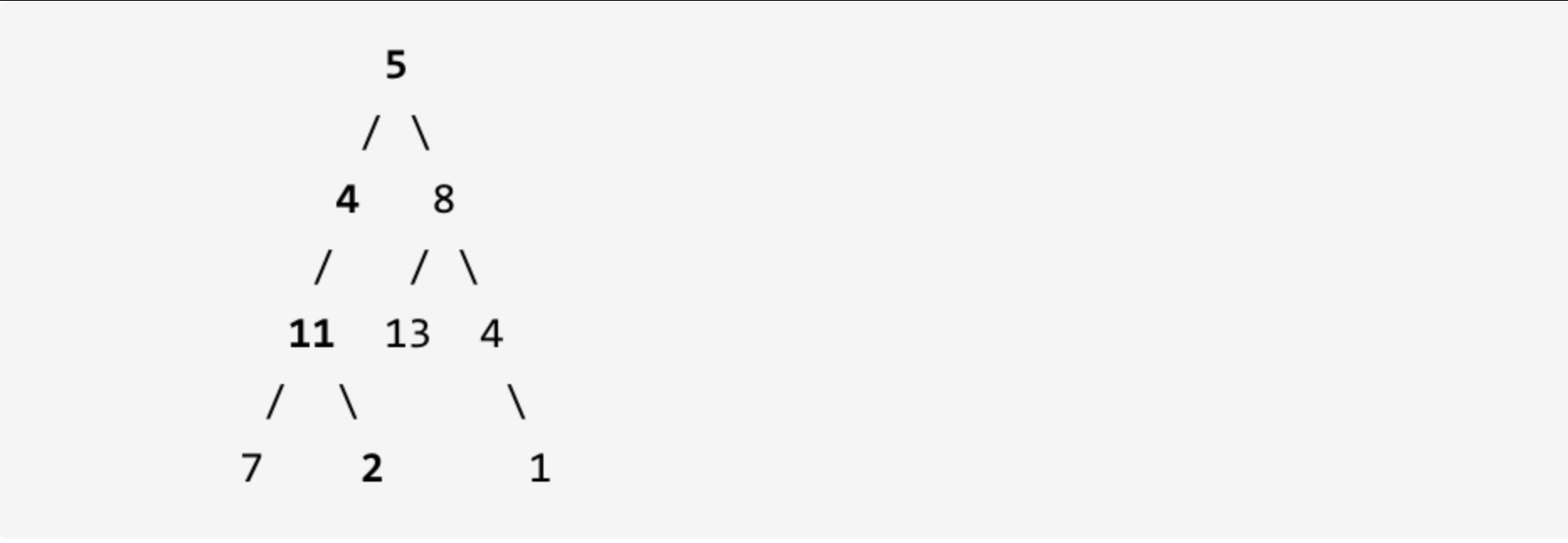
示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
递归法
优先考虑深度优先遍历,前中后序都没有区别,因为没有中的处理逻辑。

累加判断是否等于的写法有点麻烦,可以用递减法,如果count等于0就说明找到了。
class Solution {
public:bool traversal(TreeNode*cur,int count){if(!cur->left&&!cur->right&&count==0)return true;//遇到叶子节点且count为0if(!cur->left&&!cur->right)return false;//遇到叶子节点且count不为0if(cur->left){count-=cur->left->val;if(traversal(cur->left,count))return true;//如果从下一层递归里得到1返回1count+=cur->left->val;//回溯}if(cur->right){count-=cur->right->val;if(traversal(cur->right,count))return true;count+=cur->right->val;//回溯}return false;}bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {if(root==NULL)return false;return traversal(root,targetSum-root->val);}
};迭代法可以用栈模拟回溯。
113.路径总和Ⅱ
113. 路径总和 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
要遍历整棵树,所以递归函数没有返回值。

class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>>result;vector<int>path;void traversal(TreeNode*cur,int count){if(!cur->left&&!cur->right&&count==0){result.push_back(path);//找到一条路径return;}if(!cur->left&&!cur->right)return;if(cur->left)//左{count-=cur->left->val;path.push_back(cur->left->val);traversal(cur->left,count);//回溯count+=cur->left->val;path.pop_back();}if(cur->right)//左{count-=cur->right->val;path.push_back(cur->right->val);traversal(cur->right,count);//回溯count+=cur->right->val;path.pop_back();}return;}vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {result.clear();path.clear();if(root==NULL)return result;path.push_back(root->val);traversal(root,targetSum-root->val);return result;}
};也比较简单。
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
题目:106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
之前看过从中序和后序以及前序和中序构造二叉树的书本例子,所以本题理解起来不难,就是代码没有切实打过。中序是比较重要的,因为可以帮助我们区分左右子树。

来看一下一共分几步:
第一步:如果数组大小为零的话,说明是空节点了。
第二步:如果不为空,那么取后序数组最后一个元素作为节点元素。
第三步:找到后序数组最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组 (顺序别搞反了,一定是先切中序数组)
第五步:切割后序数组,切成后序左数组和后序右数组
第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
代码注意点,切割中序数组时,首先从后序数组找到了最后一个元素,就是根节点,在中序数组找到,左右分割成左中序和右中序。再根据左右中序的大小,在后序数组切割相应大小的元素, 分割前部分为左后序,后部分为右后序。以此类推,递归构造二叉树。
代码
class Solution {
private:TreeNode*traversal(vector<int>& inorder,vector<int>& postorder){if(postorder.size()==0)return NULL;int rootvalue=postorder[postorder.size()-1];//1.找到后序数组最后一个元素,即根节点TreeNode*root=new TreeNode(rootvalue);if(postorder.size()==1)return root;//如果只剩下叶子节点int delimiterIndex;//找到分割点for(delimiterIndex=0;delimiterIndex<inorder.size();delimiterIndex++){if(inorder[delimiterIndex]==rootvalue)break;}vector<int>leftinorder(inorder.begin(),inorder.begin()+delimiterIndex);//切割中序数组,左闭右开写法vector<int>rightinorder(inorder.begin()+delimiterIndex+1,inorder.end());//注意这里是+1!postorder.resize(postorder.size()-1);//移除后序数组最后一个元素//切割后序数组,注意后序和中序大小一样,所以可以以上步求得的左右中序数组大小作为分割vector<int>leftpostorder(postorder.begin(),postorder.begin()+leftinorder.size());vector<int>rightpostorder(postorder.begin()+leftinorder.size(),postorder.end());root->left=traversal(leftinorder,leftpostorder);//传入新的左中序和左后序,继续构造左右子树root->right=traversal(rightinorder,rightpostorder);return root;}
public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if(inorder.size()==0||postorder.size()==0)return NULL;return traversal(inorder,postorder);}
};今天的还行吧。没有特别难,基本都能自己写出来,但是细节还要多注意。







搜索、倒排索引)
