图的存储
邻接矩阵
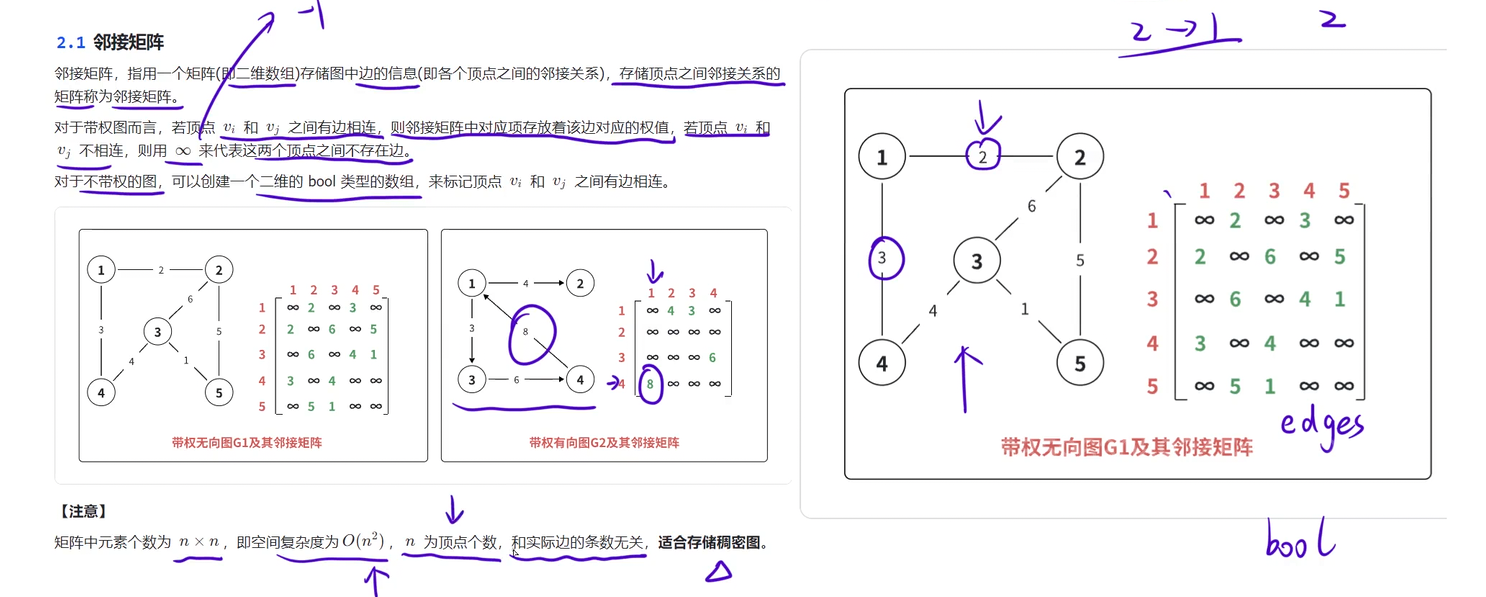
#include <iostream>#include <cstring>using namespace std;const int N = 1010;int n, m;int edges[N][N];int main()
{memset(edges, -1, sizeof edges);cin >> n >> m; // 读⼊结点个数以及边的个数 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; // a - b 有⼀条边,权值为 c edges[a][b] = c;// 如果是⽆向边,需要反过来再存⼀下 edges[b][a] = c;}
return 0;
}
邻接表
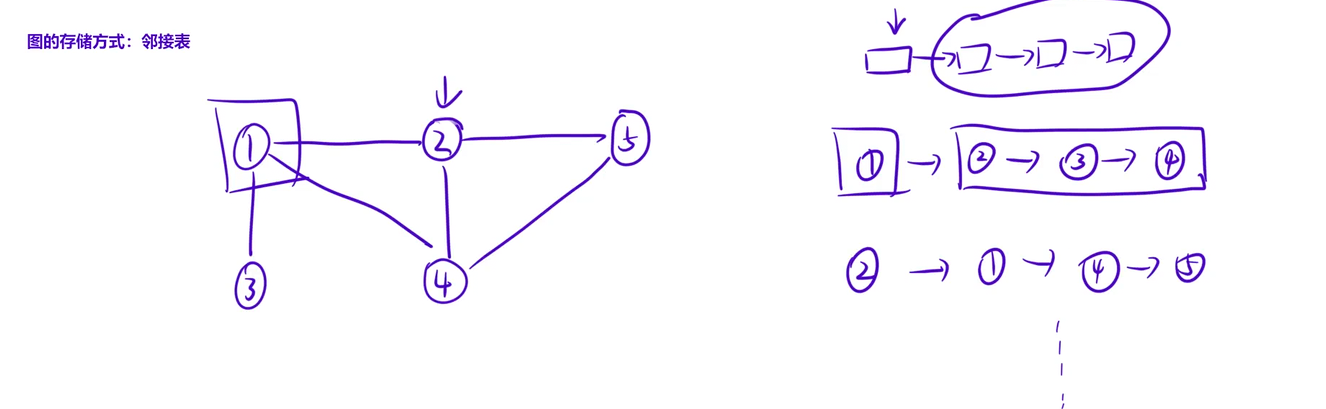
和树的存储⼀模⼀样,只不过如果存在边权的话,我们的vector数组⾥⾯放⼀个结构体或者是pair即 可。
#include <iostream>#include <vector>using namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;//那个结点,权值const int N = 1e5 + 10;int n, m;
vector<PII> edges[N];int main()
{cin >> n >> m; // 读⼊结点个数以及边的个数 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c;// a 和 b 之间有⼀条边,权值为 c edges[a].push_back({b, c});// 如果是⽆向边,需要反过来再存⼀下 edges[b].push_back({a, c});}return 0;
}
链式前向星
和树的存储⼀模⼀样,只不过如果存在边权的话,我们多创建⼀维数组,⽤来存储边的权值即可。
#include <iostream>using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 10;// 链式前向星 int h[N], e[N * 2], ne[N * 2], w[N * 2], id;int n, m;// 其实就是把 b 头插到 a 所在的链表后⾯ void add(int a, int b, int c)
{id++;e[id] = b;w[id] = c; // 多存⼀个权值信息 ne[id] = h[a];h[a] = id;
}int main()
{cin >> n >> m; // 读⼊结点个数以及边的个数 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c;// a 和 b 之间有⼀条边,权值为 c add(a, b, c); add(b, a, c);}return 0;
}
图的遍历
dfs
1.邻接矩阵
#include <iostream>#include <cstring>#include <queue>using namespace std;const int N = 1010;int n, m;int edges[N][N];bool st[N]; // 标记哪些点已经访问过 void dfs(int u)
{cout << u << endl;st[u] = true;// 遍历所有孩⼦ for(int v = 1; v <= n; v++){// 如果存在 u->v 的边,并且没有遍历过 if(edges[u][v] != -1 && !st[v]){dfs(v);}}
}int main()
{memset(edges, -1, sizeof edges);cin >> n >> m; // 读⼊结点个数以及边的个数 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; // a - b 有⼀条边,权值为 c edges[a][b] = c;// 如果是⽆向边,需要反过来再存⼀下 edges[b][a] = c;}return 0;
}
2.vector数组
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <queue>using namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;const int N = 1e5 + 10;int n, m;
vector<PII> edges[N];bool st[N]; // 标记哪些点已经访问过 void dfs(int u)
{cout << u << endl;st[u] = true;// 遍历所有孩⼦ for(auto& t : edges[u]){// u->v 的⼀条边,权值为 w int v = t.first, w = t.second;if(!st[v]) {dfs(v);}}
}int main()
{cin >> n >> m; // 读⼊结点个数以及边的个数 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c;// a 和 b 之间有⼀条边,权值为 c edges[a].push_back({b, c});// 如果是⽆向边,需要反过来再存⼀下 edges[b].push_back({a, c});}return 0;
}
bfs
邻接矩阵
#include <iostream>#include <cstring>#include <queue>using namespace std;const int N = 1010;int n, m;int edges[N][N];1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
bool st[N]; // 标记哪些点已经访问过 void bfs(int u)
{queue<int> q;q.push(u);st[u] = true;while(q.size()){auto a = q.front(); q.pop();cout << a << endl;for(int b = 1; b <= n; b++){if(edges[a][b] != -1 && !st[b]){q.push(b);st[b] = true;}}}
}int main()
{memset(edges, -1, sizeof edges);cin >> n >> m; // 读⼊结点个数以及边的个数 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; // a - b 有⼀条边,权值为 c edges[a][b] = c;// 如果是⽆向边,需要反过来再存⼀下 edges[b][a] = c;}return 0;
}
vector数组
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <queue>using namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;const int N = 1e5 + 10;int n, m;
vector<PII> edges[N];bool st[N]; // 标记哪些点已经访问过 void bfs(int u)
{queue<int> q;q.push(u);st[u] = true;while(q.size()){auto a = q.front(); q.pop();cout << a << endl;for(auto& t : edges[a]){int b = t.first, c = t.second;if(!st[b]){q.push(b);st[b] = true;}}}
}int main()
{cin >> n >> m; // 读⼊结点个数以及边的个数 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c;// a 和 b 之间有⼀条边,权值为 c edges[a].push_back({b, c});// 如果是⽆向边,需要反过来再存⼀下 edges[b].push_back({a, c});}return 0;
}







