一、稀疏镜像升级背景
常用系统镜像格式为原始镜像,即RAW格式。镜像体积比较大,在烧录固件或者升级固件时比较耗时,而且在移动设备升级过程时比较耗费流量。为此,将原始镜像用稀疏描述,可以大大地缩减镜像体积,省时省流量。
二、稀疏镜像原理
1、稀疏镜像的概念
原始镜像:即raw image,完整的ext4分区镜像,包含很多全零的无效填充区
稀疏镜像:即sparse image,将raw ext4进行稀疏描述,因此尺寸比较小,制作目录有多少文件就计算多少,没有全零填充
2、稀疏镜像格式

稀疏镜像数据格式:首先是sparse_header占用28byte,然后是12byte的chunk_header,同样这chunk_header的类型决定了后面跟着的数据,如果读到数据是0xCAC1意味着后面是本身的raw_data,如果是0xCAC3,则后面num为0,接着再0xCAC2意味着后面填充4byte的内容。
三、实现稀疏镜像升级方案
版本基线:
OpenAtom OpenHarmony(以下简称“OpenHarmony”) 3.1 Release
1、稀疏镜像烧录
(1)生成稀疏格式镜像
有2种方法可以生成稀疏镜像:
1)修改文件build/ohos_var.gni中,sparse_image=true

2)编译命令增加–sparse-image字段,如./build.sh --product-name=xxx --sparse-image
(2)增加稀疏格式转换工具
在目录build/ohos/images/mkimage中增加文件img2simg,该工具用于编译完成后将raw镜像转换为sparse格式,并设置权限为777。
(3)编译后的镜像对比

编译出的镜像格式为sparse格式,镜像大小相比raw格式明显变小。
(4)烧录稀疏镜像
烧录稀疏镜像方法和烧录原始镜像方法一致。
稀疏镜像本身是不能直接挂载的,在烧录过程中通过uboot将稀疏格式镜像还原为原始镜像,然后写到磁盘中,系统启动后可挂载对应的镜像。
2、稀疏镜像升级
升级包采用稀疏镜像制作。
(1)修改升级包制作工具
官方升级包工具不支持生成稀疏镜像的升级包,修改升级包工具,生成稀疏格式的升级包。.\base\update\packaging_tools\image_class.py

按照上图所示注释代码
(2)生成稀疏镜像升级包
和全量镜像升级包制作方法一致。
(3)适配updater组件中稀疏镜像功能
● 增加写稀疏镜像分支
.\base\update\updater\services\applypatch\data_writer.cpp
写数据函数CreateDataWriter增加写稀疏镜像分支
case WRITE_SPARSE:
{std::unique_ptr<SparseWriter> writer(std::make_unique<SparseWriter>(partitionName));return std::move(writer);
}
● 增加稀疏镜像类声明
.\base\update\updater\services\applypatch\raw_writer.h
增加稀疏镜像类声明及相关变量定义
typedef struct sparse_header {uint32_t magic; /* 0xed26ff3a */uint16_t major_version; /* (0x1) - reject images with higher major versions */uint16_t minor_version; /* (0x0) - allow images with higer minor versions */uint16_t file_hdr_sz; /* 28 bytes for first revision of the file format */uint16_t chunk_hdr_sz; /* 12 bytes for first revision of the file format */uint32_t blk_sz; /* block size in bytes, must be a multiple of 4 (4096) */uint32_t total_blks; /* total blocks in the non-sparse output image */uint32_t total_chunks; /* total chunks in the sparse input image */uint32_t image_checksum; /* CRC32 checksum of the original data, counting "don't care" *//* as 0. Standard 802.3 polynomial, use a Public Domain *//* table implementation */
} sparse_header_t;#define SPARSE_HEADER_MAGIC 0xed26ff3a#define CHUNK_TYPE_RAW 0xCAC1
#define CHUNK_TYPE_FILL 0xCAC2
#define CHUNK_TYPE_DONT_CARE 0xCAC3
#define CHUNK_TYPE_CRC32 0xCAC4typedef struct chunk_header {uint16_t chunk_type; /* 0xCAC1 -> raw; 0xCAC2 -> fill; 0xCAC3 -> don't care */uint16_t reserved1;uint32_t chunk_sz; /* in blocks in output image */uint32_t total_sz; /* in bytes of chunk input file including chunk header and data */
} chunk_header_t;class SparseWriter : public DataWriter {
public:virtual bool Write(const uint8_t *addr, size_t len, WriteMode mode, const std::string &partitionName);explicit SparseWriter(const std::string partitionName) : offset_(0), fd_(-1), partitionName_(partitionName) {}virtual ~SparseWriter(){offset_ = 0;if (fd_ > 0) {fsync(fd_);close(fd_);}fd_ = -1;}
private:int WriteInternal(int fd, const uint8_t *data, size_t len, const std::string &partitionName);SparseWriter(const SparseWriter&) = delete;const SparseWriter& operator=(const SparseWriter&) = delete;off64_t offset_;int fd_;std::string partitionName_;
};
● 增加稀疏镜像类实现
.\base\update\updater\services\applypatch\raw_writer.cpp
增加稀疏镜像类实现及相关变量定义,原有代码不变
bool SparseWriter::Write(const uint8_t *addr, size_t len, WriteMode mode, const std::string &partitionName)
{if (addr == nullptr) {LOG(ERROR) << "SparseWriter: invalid address.";return false;}if (len == 0) {LOG(INFO) << "SparseWriter: write length is 0, skip.";return false;}if (fd_ < 0) {fd_ = OpenPartition(partitionName_);if (fd_ < 0) {return false;}}UPDATER_CHECK_ONLY_RETURN(WriteInternal(fd_, addr, len, partitionName_) >= 0, return false);return true;
}int SparseWriter::WriteInternal(int fd, const uint8_t *data, size_t len, const std::string &partitionName)
{uint32_t written = 0;sparse_header_t *sparse_header;chunk_header_t *chunk_header;unsigned int chunk;void *membuf = NULL;uint32_t *fill_buf = NULL;uint32_t fill_val;uint32_t bytes_written = 0;uint32_t total_bytes = 0;uint32_t blk = 0;uint32_t chunk_data_sz = 0;uint32_t blkcnt = 0;uint32_t blks = 0;uint32_t total_blocks = 0;uint32_t addr_offset = 0;uint32_t fill_buf_num_blks = 0;uint32_t block_size = 4096;uint32_t block_count = 524288;uint32_t i;uint32_t j;int ret = lseek64(fd, offset_, SEEK_SET);UPDATER_FILE_CHECK(ret != -1, "RawWriter: failed to seek file to " << offset_, return -1);fill_buf_num_blks = CONFIG_FASTBOOT_FLASH_FILLBUF_SIZE / block_size;LOG(INFO) << "WriteInternal offset_ " << offset_;/* Read and skip over sparse image header */sparse_header = (sparse_header_t *)data;data += sparse_header->file_hdr_sz;if (sparse_header->file_hdr_sz > sizeof(sparse_header_t)) {/** Skip the remaining bytes in a header that is longer than* we expected.*/data += (sparse_header->file_hdr_sz - sizeof(sparse_header_t));}LOG(INFO) << "=== Sparse Image Header ===";LOG(INFO) << "magic: " << sparse_header->magic;
LOG(INFO)<<"major_version: "<< sparse_header->major_version;
LOG(INFO)<<"minor_version: "<< sparse_header->minor_version;
LOG(INFO)<<"file_hdr_sz: "<< sparse_header->file_hdr_sz;
LOG(INFO)<<"chunk_hdr_sz: "<< sparse_header->chunk_hdr_sz;
LOG(INFO)<<"blk_sz: "<< sparse_header->blk_sz;
LOG(INFO)<<"total_blks: "<< sparse_header->total_blks;
LOG(INFO)<<"total_chunks: "<< sparse_header->total_chunks;LOG(INFO)<<"Flashing Sparse Image";blk =0;
for(chunk =0; chunk < sparse_header->total_chunks; chunk++){
/* Read and skip over chunk header */chunk_header =(chunk_header_t*)data;data +=sizeof(chunk_header_t);
if(chunk_header->chunk_type != CHUNK_TYPE_RAW)
{
LOG(INFO)<<"=== Chunk Header ===";
LOG(INFO)<<"chunk_type: "<< chunk_header->chunk_type;
LOG(INFO)<<"chunk_sz: "<< chunk_header->chunk_sz;
LOG(INFO)<<"total_sz: "<< chunk_header->total_sz;
}
if(sparse_header->chunk_hdr_sz >sizeof(chunk_header_t)){
/** Skip the remaining bytes in a header that is longer* than we expected.*/data +=(sparse_header->chunk_hdr_sz -
sizeof(chunk_header_t));
}chunk_data_sz = sparse_header->blk_sz * chunk_header->chunk_sz;blkcnt = chunk_data_sz / block_size;
switch(chunk_header->chunk_type){
case CHUNK_TYPE_RAW:
if(chunk_header->total_sz !=
(sparse_header->chunk_hdr_sz + chunk_data_sz)){
LOG(ERROR)<<"Bogus chunk size for chunk type Raw";
return-1;
}
if(blk + blkcnt >0+ block_count){
LOG(ERROR)<<"Request would exceed partition size!";
return-1;
}addr_offset = blk * block_size;ret =lseek64(fd, offset_ + addr_offset,SEEK_SET);
if(ret <0){
LOG(ERROR)<<"failed to seek file to "<< addr_offset <<" error="<<strerror(errno);
return-1;
}written =write(fd, data, blkcnt * block_size);
if(written <0){
LOG(ERROR)<<"SparseWriter: failed to write data of len ";
return-1;
}total_bytes = total_bytes + blkcnt * block_size;blks = written / block_size;blk += blks;bytes_written += blkcnt * block_size;total_blocks += chunk_header->chunk_sz;data += chunk_data_sz;
break;
case CHUNK_TYPE_FILL:
if(chunk_header->total_sz !=
(sparse_header->chunk_hdr_sz +sizeof(uint32_t))){
LOG(ERROR)<<"Bogus chunk size for chunk type FILL total_sz err "<< chunk_header->total_sz <<"\n";
return-1;
}ret =posix_memalign(&membuf,64,
ROUNDUP(block_size * fill_buf_num_blks,
64));
if(ret){
LOG(ERROR)<<"posix_memalign:"<<strerror(errno);
return-1;
}fill_buf =(uint32_t*)membuf;
if(!fill_buf){
LOG(ERROR)<<"Malloc failed for: CHUNK_TYPE_FILL";
return-1;
}fill_val =*(uint32_t*)data;data = data +sizeof(uint32_t);
for(i =0;i <(block_size * fill_buf_num_blks /
sizeof(fill_val));i++)fill_buf[i]= fill_val;
if(blk + blkcnt >0+ block_count){
LOG(ERROR)<<"Request would exceed partition size!";
return-1;
}
for(i =0; i < blkcnt;){j = blkcnt - i;
if(j > fill_buf_num_blks)j = fill_buf_num_blks;addr_offset = blk * block_size;ret =lseek64(fd, offset_ + addr_offset,SEEK_SET);
if(ret <0){
LOG(ERROR)<<"failed to lseek file to "<< addr_offset <<" error="<<strerror(errno);
return-1;
}written =write(fd, fill_buf, j * block_size);
if(written <0){
LOG(ERROR)<<"SparseWriter: failed to write data of len ";
return-1;
}total_bytes = total_bytes + j * block_size;blks = written / block_size;
if(blks < j){
LOG(ERROR)<<"Write failed, block";
free(fill_buf);
return-1;
}blk += blks;i += j;
}bytes_written += blkcnt * block_size;total_blocks += chunk_data_sz / sparse_header->blk_sz;
free(fill_buf);
break;
case CHUNK_TYPE_DONT_CARE:blk += blkcnt;total_blocks += chunk_header->chunk_sz;
break;
case CHUNK_TYPE_CRC32:
if(chunk_header->total_sz !=sparse_header->chunk_hdr_sz){
LOG(ERROR)<<"Bogus chunk size for chunk type CRC32 total_sz err "<< chunk_header->total_sz;
return-1;
}total_blocks += chunk_header->chunk_sz;data += chunk_data_sz;
break;
default:
LOG(INFO)<<__func__<<": Unknown chunk type: "<< chunk_header->chunk_type;
return-1;
}
}
LOG(INFO)<<"Wrote "<< chunk <<"blocks, expected to write "<< sparse_header->total_blks <<"blocks\n";
LOG(INFO)<<"........ wrote "<< bytes_written <<"bytes to "<< partitionName <<"\n";
LOG(INFO)<<"total_bytes="<< total_bytes;
return0;
}
3、验证稀疏镜像升级
(1)拷贝升级包
将制作的稀疏镜像升级包通过HDC工具推进系统data目录,并修改文件名为updater.zip,路径如下:/data/updater/updater.zip
(2)启动升级
系统启动后,在命令行工具输入如下命令启动升级
reboot updater:–update_package=/data/updater/updater.zip
输入命令后,系统重启,进入升级页面,等待升级完成。
本文介绍了OpenHarmony系统中实现稀疏镜像升级的方法,理解稀疏镜像原理及稀疏镜像还原方法可以快速在自己的系统中应用稀疏镜像升级,提高系统升级速度。
经常有很多小伙伴抱怨说:不知道学习鸿蒙开发哪些技术?不知道需要重点掌握哪些鸿蒙应用开发知识点?
为了能够帮助到大家能够有规划的学习,这里特别整理了一套纯血版鸿蒙(HarmonyOS Next)全栈开发技术的学习路线,包含了鸿蒙开发必掌握的核心知识要点,内容有(ArkTS、ArkUI开发组件、Stage模型、多端部署、分布式应用开发、WebGL、元服务、OpenHarmony多媒体技术、Napi组件、OpenHarmony内核、OpenHarmony驱动开发、系统定制移植等等)鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)技术知识点。

《鸿蒙 (Harmony OS)开发学习手册》(共计892页):https://gitcode.com/HarmonyOS_MN/733GH/overview
如何快速入门?
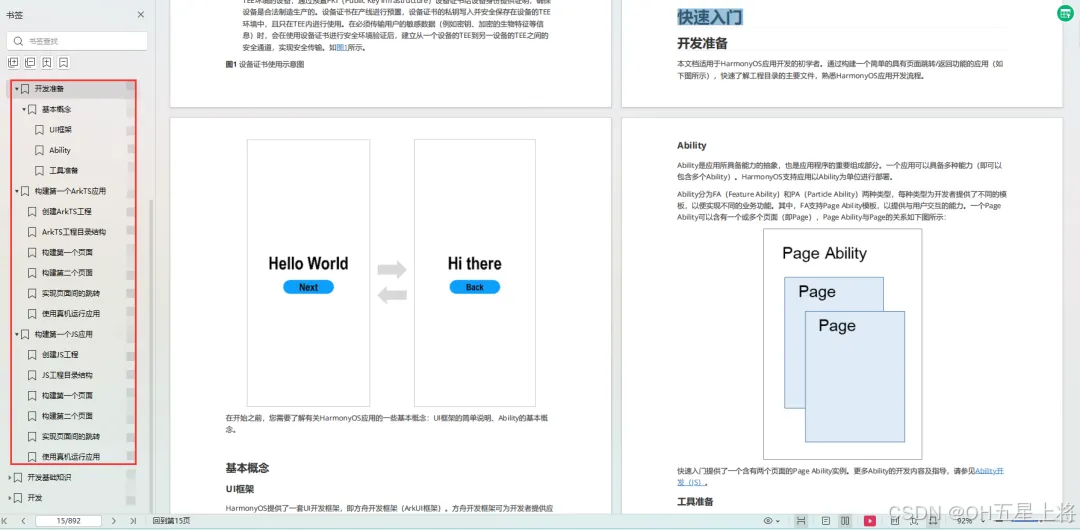
1.基本概念
2.构建第一个ArkTS应用
3.……
开发基础知识:
1.应用基础知识
2.配置文件
3.应用数据管理
4.应用安全管理
5.应用隐私保护
6.三方应用调用管控机制
7.资源分类与访问
8.学习ArkTS语言
9.……

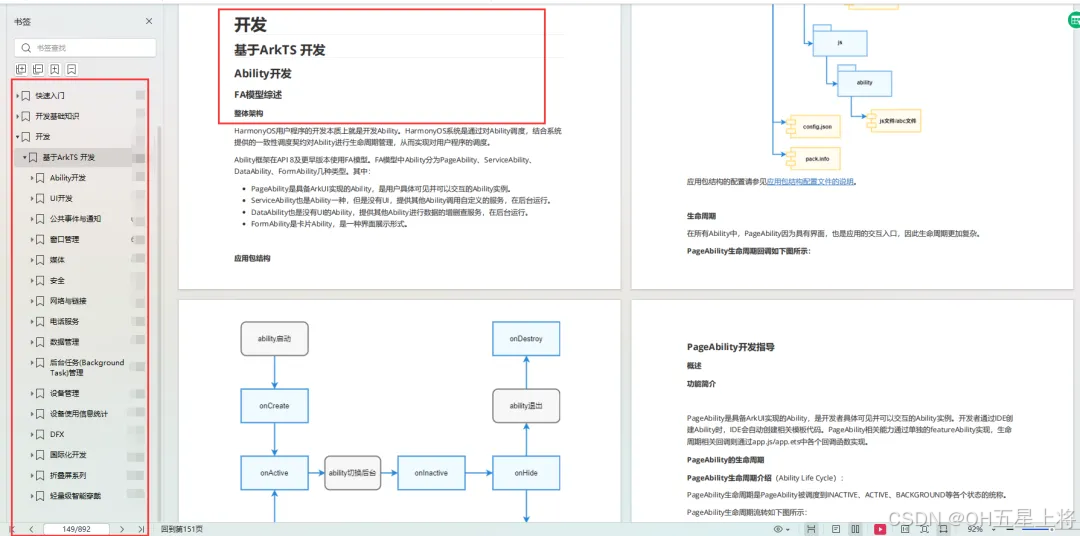
基于ArkTS 开发
1.Ability开发
2.UI开发
3.公共事件与通知
4.窗口管理
5.媒体
6.安全
7.网络与链接
8.电话服务
9.数据管理
10.后台任务(Background Task)管理
11.设备管理
12.设备使用信息统计
13.DFX
14.国际化开发
15.折叠屏系列
16.……
鸿蒙开发面试真题(含参考答案):https://gitcode.com/HarmonyOS_MN/733GH/overview
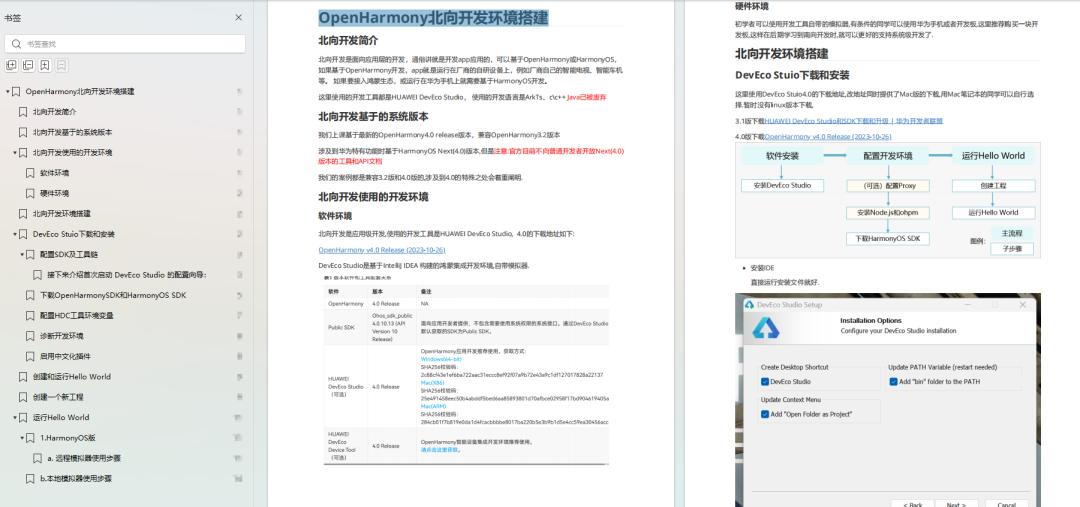
OpenHarmony 开发环境搭建
《OpenHarmony源码解析》:https://gitcode.com/HarmonyOS_MN/733GH/overview
- 搭建开发环境
- Windows 开发环境的搭建
- Ubuntu 开发环境搭建
- Linux 与 Windows 之间的文件共享
- ……
- 系统架构分析
- 构建子系统
- 启动流程
- 子系统
- 分布式任务调度子系统
- 分布式通信子系统
- 驱动子系统
- ……

OpenHarmony 设备开发学习手册:https://gitcode.com/HarmonyOS_MN/733GH/overview









