今天,我们探讨一下 Vue 中的组件传值问题。这不仅是我们在日常开发中经常遇到的核心问题,也是面试过程中经常被问到的重要知识点。无论你是初学者还是有一定经验的开发者,掌握这些传值方式都将帮助你更高效地构建和维护 Vue 应用

目录
1. 父子组件通信
2. 事件总线通信
3. 路由传参
4. Vuex 状态管理
1. 父子组件通信
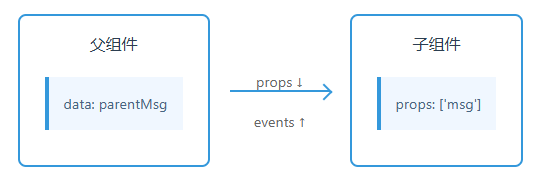
// 父组件
<child-component :msg="parentMsg"@update="handleUpdate"
/>// 子组件
props: ['msg'],
methods: {updateParent() {this.$emit('update', newValue)}
}一、完整实现流程
1. 父组件传递数据
核心机制:通过 props 向下传递数据
<template><!-- 绑定 props 与事件监听 --><child-component :msg="parentMsg" @update="handleUpdate"/>
</template><script>
export default {data() {return {parentMsg: "来自父组件的消息" // 初始数据}},methods: {handleUpdate(newValue) {this.parentMsg = newValue // 更新父组件数据}}
}
</script>2. 子组件接收与响应
核心机制:通过 props 接收数据,通过 $emit 触发事件
<script>
export default {props: {msg: {type: String, // 类型校验default: '' // 默认值}},methods: {updateParent() {const newValue = "修改后的消息"this.$emit('update', newValue) // 触发自定义事件}}
}
</script>3、数据流向示意图
父组件 子组件
[parentMsg] --props--> (msg)↑ ||-- event update <----4、关键特性说明
-
单向数据流
-
数据只能通过 props 从父级流向子级
-
禁止在子组件中直接修改 props(需通过事件触发父级修改)
-
事件触发规范
-
推荐使用 kebab-case 事件名(如
update-data) -
可通过对象形式传递复杂数据
this.$emit('update', { value: newValue,timestamp: Date.now()
})-
生命周期影响
-
父组件的 data 更新会触发子组件的重新渲染
-
可通过
watch监听 props 变化
watch: {msg(newVal) {// 响应父组件数据更新}
}二、进阶实现模式
1. 双向绑定简化(v-model)
<!-- 父组件 -->
<child-component v-model="parentMsg" /><!-- 子组件 -->
<script>
export default {model: {prop: 'msg',event: 'update'},props: ['msg']
}
</script>2. 跨层级通信
-
使用 provide/inject(需谨慎设计)
-
使用 Vuex/Pinia 状态管理(复杂场景推荐)
三、常见问题处理
1.Prop 验证失败
props: {msg: {type: String,required: true,validator: value => value.length > 5}
}2.异步更新处理
this.$nextTick(() => {this.$emit('update', asyncData)
})3.事件解绑建议
// 父组件销毁时自动解绑
// 需要手动解绑的特殊场景:
beforeDestroy() {this.$off('update')
}四、最佳实践建议
-
保持 props 的纯净性(仅用于显示/基础逻辑)
-
复杂交互建议使用 Vuex 进行状态管理
-
大型项目推荐使用 TypeScript 定义 props 接口
-
使用自定义事件时添加命名空间(如
user:updated)
2. 事件总线通信
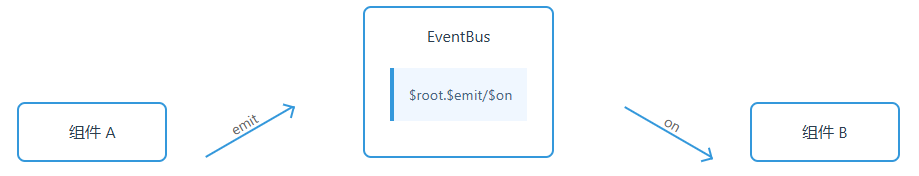
// 组件 A
this.$root.$emit('event-name', data)// 组件 B
created() {this.$root.$on('event-name', this.handler)
}
beforeDestroy() {this.$root.$off('event-name', this.handler)
}一、核心概念
事件总线:一个中央事件处理中心,用于组件间跨层级通信(父子/兄弟/任意组件)。
通信原理:
组件A --emit()--> EventBus --on()--> 组件B二、完整实现流程
1. 创建事件总线
// event-bus.js
import Vue from 'vue'
export const EventBus = new Vue()2. 组件A发送事件
<!-- ComponentA.vue -->
<script>
import { EventBus } from './event-bus.js'export default {methods: {sendData() {// 触发事件并传递数据EventBus.$emit('custom-event', {message: '来自组件A的数据',timestamp: Date.now()})}}
}
</script>3. 组件B监听事件
<!-- ComponentB.vue -->
<script>
import { EventBus } from './event-bus.js'export default {created() {// 注册事件监听EventBus.$on('custom-event', this.handleEvent)},beforeDestroy() {// 必须!销毁前移除监听EventBus.$off('custom-event', this.handleEvent)},methods: {handleEvent(payload) {console.log('收到数据:', payload)// 可在此处更新组件状态或触发其他操作}}
}
</script>三、关键代码解析
| 方法 | 作用 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|---|
|
| 触发自定义事件 |
|
|
| 监听指定事件 |
|
|
| 移除指定事件监听 |
|
四、高级用法
1. 一次性监听
EventBus.$once('one-time-event', this.handleOnce)2. 全局事件总线(使用根实例)
// 组件内发送事件
this.$root.$emit('global-event', data)// 组件内监听事件
this.$root.$on('global-event', callback)3. 事件命名规范
// 推荐格式:领域/操作
EventBus.$emit('user/profile-updated', userData)五、生命周期管理
-
必须在
beforeDestroy中移除监听,避免:-
内存泄漏
-
重复触发僵尸监听器
-
-
自动移除方案:
// 使用 hook API 自动解绑
mounted() {this.$eventBus.$on('event', callback)this.$once('hook:beforeDestroy', () => {this.$eventBus.$off('event', callback)})
}六、注意事项
1.数据不可变性
传递的数据应为副本而非引用:
EventBus.$emit('event', { ...originalObject })2.调试技巧
查看所有事件监听:
console.log(EventBus._events)3.性能优化
高频事件建议添加防抖:
import _ from 'lodash'
EventBus.$on('scroll', _.debounce(this.handleScroll, 200))七、与Vuex的对比
| EventBus | Vuex | |
|---|---|---|
| 适用场景 | 简单通信/临时交互 | 复杂状态管理 |
| 数据存储 | 无中心化存储 | 集中式状态存储 |
| 调试支持 | 无Devtools集成 | 完整时间旅行调试 |
| 推荐使用 | 小型项目/简单交互 | 中大型项目 |
八、完整代码示例
// 组件A:发送方
methods: {notify() {this.$root.$emit('notify', { type: 'alert',content: '重要通知' })}
}// 组件B:接收方
created() {this.$root.$on('notify', this.showNotification)
},
beforeDestroy() {this.$root.$off('notify', this.showNotification)
},
methods: {showNotification(payload) {if(payload.type === 'alert') {alert(payload.content)}}
}流程图解
组件A EventBus 组件B
[点击按钮] --> $emit('event') --> 事件队列 --> 匹配监听器 --> $on('event') --> 执行回调↖---------------------------数据载荷---------------------------↙最佳实践
-
为事件总线创建独立模块
- 使用TypeScript定义事件类型
// event-types.d.ts declare module 'vue/types/vue' {interface Vue {$eventBus: {$on(event: 'user-login', callback: (user: User) => void): void$emit(event: 'user-login', user: User): void}} } -
大型项目建议封装为可追踪的EventService
-
重要事件添加错误边界处理
3. 路由传参
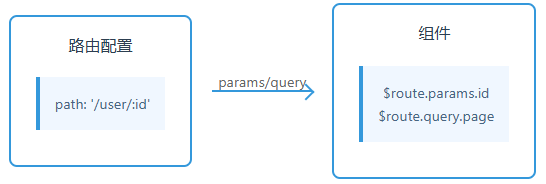
// 路由跳转
this.$router.push({name: 'User',params: { id: 123 },query: { page: 1 }
})// 组件中获取
created() {const userId = this.$route.params.idconst page = this.$route.query.page
}一、完整实现流程
1. 路由配置(核心配置)
// router/index.js
{path: "/user/:id", // 动态路由参数(注意冒号语法)name: "UserDetail", // 推荐使用命名路由(非图片中的"I','user"错误写法)component: UserComponent
}2. 路由跳转
// 正确写法(修正图片中的符号错误和拼写错误)
this.$router.push({name: 'UserDetail', // 使用路由名称更安全(而非图片中的"I','user"错误写法)params: { id: 123 }, // 路径参数(对应:id)query: { page: 1 } // 查询参数(URL显示为?page=1)
})3. 组件参数获取
created() {// 正确获取方式(修正图片中的符号错误)const userId = this.$route.params.id // 获取路径参数(非图片中的"parc�名"错误)const page = this.$route.query.page // 获取查询参数(非图片中的".php"错误)console.log(`用户ID: ${userId}, 当前页: ${page}`)
}二、核心概念解析
1. 参数类型对比
| params | query | |
|---|---|---|
| URL显示 |
|
|
| 参数位置 | 路径中 | URL问号后 |
| 路由配置 | 需要预定义 | 无需预先声明 |
| 参数类型 | 自动转为字符串 | 自动转为字符串 |
| 刷新保留 | 是(需配合命名路由使用) | 是 |
2. 生命周期响应
watch: {// 监听路由参数变化(图片未展示的重要功能)'$route'(to, from) {if (to.params.id !== from.params.id) {this.loadUserData(to.params.id)}}
}三、代码优化建议
1. 类型转换处理
// 将字符串参数转为数字(图片未展示)
created() {this.userId = parseInt(this.$route.params.id)this.page = Number(this.$route.query.page) || 1
}2. 使用Props接收参数(推荐方式
// 路由配置增加(图片未展示)
props: true// 组件接收(更规范的写法)
props: {id: {type: [Number, String],required: true}
}四、常见问题处理
1. params失效问题
// 错误写法(图片中写法会导致params丢失)
this.$router.push({path: '/user/123', // 使用path时params会失效params: { id: 456 } // 此参数不会被传递
})// 正确写法(必须使用name)
this.$router.push({name: 'UserDetail',params: { id: 456 }
})2. 参数继承方案
// 保持现有查询参数(图片未展示)
this.$router.push({params: { id: 789 },query: { ...this.$route.query } // 保留原有查询参数
})五、完整代码示例
路由配置
// router/index.js
{path: '/user/:id',name: 'UserDetail',component: () => import('./views/UserDetail.vue'),props: true // 启用props接收参数
}路由跳转
methods: {navigate() {this.$router.push({name: 'UserDetail',params: { id: 2023 },query: { page: 2,sort: 'desc'}})}
}组件实现
<template><div><h2>用户ID: {{ formattedId }}</h2><p>当前页码: {{ page }}</p></div>
</template><script>
export default {props: {id: {type: Number,required: true}},computed: {formattedId() {return `UID-${this.id.toString().padStart(6, '0')}`},page() {return Number(this.$route.query.page) || 1}},watch: {id(newVal) {this.loadUserData(newVal)}},methods: {loadUserData(id) {// 加载用户数据...}}
}
</script>六、最佳实践建议
-
参数验证:
// 路由配置添加正则约束
path: '/user/:id(\\d+)' // 只接受数字ID// 组件内验证
beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) {if (!/^\d+$/.test(to.params.id)) {next({ name: 'ErrorPage' })} else {next()}
}-
编码规范:
-
始终使用命名路由(避免路径硬编码)
-
敏感参数使用params传递(不在URL暴露)
-
复杂参数使用JSON序列化:
this.$router.push({name: 'Search',query: {filters: JSON.stringify({ status: ['active', 'pending'],dateRange: '2023-01/2023-12'})}
})流程图解
[路由跳转]│├── params → /user/:id│ └──→ 组件通过 $route.params 或 props 接收│└── query → ?key=value└──→ 组件通过 $route.query 接收常见错误排查表
| 现象 | 原因 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
| params参数未传递 | 使用了path而非name进行跳转 | 改用命名路由 |
| 参数丢失 | 未处理路由守卫中的中断 | 添加路由守卫参数验证 |
| 参数类型错误 | 未进行类型转换 | 使用Number()或parseInt转换 |
| 组件未响应参数变化 | 缺少watch监听 | 添加$route监听 |
4. Vuex 状态管理

// 组件中使用
export default {computed: {...mapState(['data']),...mapGetters(['processedData'])},methods: {updateData() {this.$store.dispatch('updateAction', payload)}}
}一、完整实现流程
1. 安装与配置
npm install vuex --save// store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'Vue.use(Vuex)export default new Vuex.Store({state: { offers: [], data: [] },mutations: { /* 同步修改方法 */ },actions: { /* 异步操作方法 */ },getters: { /* 计算属性方法 */ },modules: { /* 模块划分 */ }
})2. 核心流程
组件 → dispatch → Actions → commit → Mutations → 修改 State → 触发视图更新二、核心概念详解
1. State(应用状态)
state: {offers: [],data: []
}// 组件访问
this.$store.state.offers2. Mutations(同步修改)
mutations: {SET_OFFERS(state, payload) {state.offers = payload}
}// 组件触发(禁止直接调用)
this.$store.commit('SET_OFFERS', newData)3. Actions(异步操作)
actions: {async fetchOffers({ commit }) {const res = await axios.get('/api/offers')commit('SET_OFFERS', res.data)}
}// 组件触发
this.$store.dispatch('fetchOffers')4. Getters(计算属性)
getters: {processedData: state => {return state.data.filter(item => item.status === 1)}
}// 组件访问
this.$store.getters.processedData三、组件集成方案
1. mapState/mapGetters
import { mapState, mapGetters } from 'vuex'export default {computed: {...mapState({data: state => state.data}),...mapGetters(['processedData'])}
}2. Action分发
methods: {updateData() {// 修正原图片中的拼写错误this.$store.dispatch('updateAction', payload)}
}四、模块化实现
// store/modules/user.js
export default {namespaced: true,state: { profile: null },mutations: { SET_PROFILE(state, val) {...} },actions: { fetchProfile({ commit }) {...} }
}// 组件访问
this.$store.dispatch('user/fetchProfile')五、完整代码示例
// 组件完整实现
export default {computed: {...mapState({offers: state => state.offers}),...mapGetters(['filteredOffers'])},methods: {refreshData() {this.$store.dispatch('fetchOffers')},updateOffer(payload) {this.$store.commit('UPDATE_OFFER', payload)}}
}六、数据流向示意图
Component → dispatch → Action → commit → Mutation → State → Getter → Component↑ ↓└─────── API 请求/异步操作 ────────────┘七、高级特性
1. 严格模式
const store = new Vuex.Store({strict: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
})2. 插件开发
// 状态快照插件
const snapshotPlugin = store => {let prevState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(store.state))store.subscribe((mutation, state) => {console.log('状态变化:', mutation.type)console.log('旧状态:', prevState)console.log('新状态:', state)prevState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state))})
}八、常见问题处理
1. 异步操作错误处理
actions: {async fetchData({ commit }) {try {const res = await api.getData()commit('SET_DATA', res.data)} catch (error) {commit('SET_ERROR', error.message)}}
}2. 动态模块注册
store.registerModule('dynamicModule', {state: {...},mutations: {...}
})九、最佳实践建议
-
命名规范:
-
Mutation类型使用全大写(SET_DATA)
-
Action名称使用驼峰命名(fetchUserInfo)
-
-
模块组织:
/store├── index.js├── modules│ ├── user.js│ └── product.js└── plugins -
TypeScript集成:
// store/types.ts
interface RootState {user: UserStateproducts: ProductState
}// 组件使用
@Action
public async updateProfile(payload: UserProfile) {this.context.commit('SET_PROFILE', payload)
}-
性能优化:
-
避免在getter中进行重计算
-
使用Vuex的持久化插件(vuex-persistedstate)
-
十、调试技巧
-
DevTools时间旅行:
-
查看状态快照
-
回退/重做mutation
-
-
状态快照输出:
console.log(JSON.stringify(this.$store.state, null, 2))完整流程图解
[Component] │ dispatch(action) ↓
[Action] → 发起API请求 → commit(mutation)│ ↓└─────────────→ [Mutation] → 修改State↓[Getter] → 派生状态↓[Component] 响应式更新好了这一期就到这里,希望能够帮助到大家,咱们下下期见!


)
感知机)


