DFS和BFS基础
做图论这部分的题目DFS和BFS少不了
DFS是深搜 沿着一条路一直搜索下去直到无法继续向下 再通过回溯 换一条路进行搜索
BFS是广搜 就是从当前节点出发 一直把当前节点所连接的所有节点都搜索过之后 进入下一节点在开始相同的搜索过程
98.所有可达路径
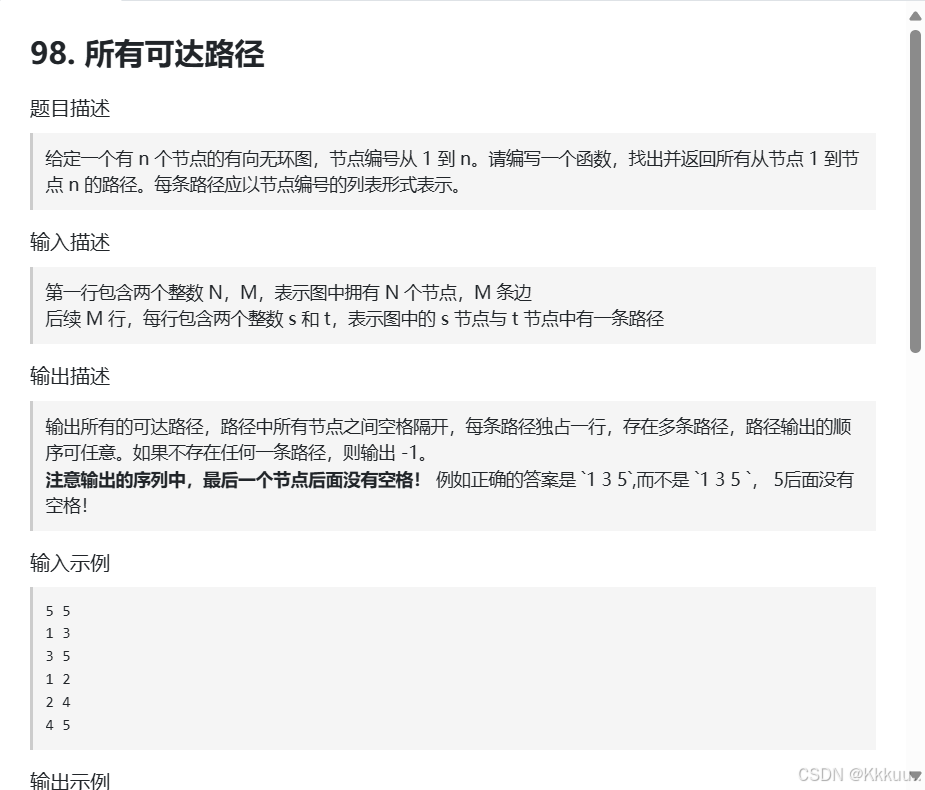
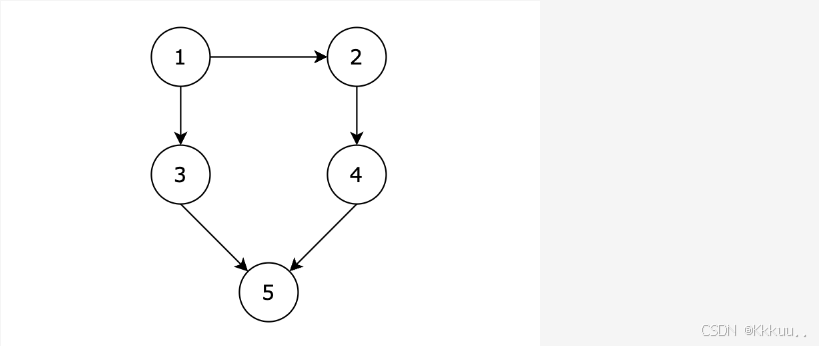
题意很简单 从1节点出发可以到5节点的所有路径 用邻接矩阵构造图 用path记录路径 ans记录所有的路径
dfs 从一条路走到底 遍历当前节点所连接的节点 放入path路径里 然后再进入dfs深搜中 下一个语句就是回溯语句 从path里删除刚刚放入的元素
void dfs(const vector<vector<int>>& graph, int x, int n){if(x==n){ans.push_back(path);}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(graph[x][i]==1){path.push_back(i);dfs(graph,i,n);path.pop_back();}}
}99. 岛屿数量

本题规定了只有上下左右四个方向 相连起来的就是一个岛屿 本题要求存在的岛屿数量
dfs
首先我们需要需要一个dir数组规定四个方向 在主函数里面如果遇到没有访问过的陆地 就让岛屿的总数加1 然后进入dfs
dfs里面逻辑 如果访问的节点访问过或者是水域 就退出dfs 如果是没访问过的陆地就标记为访问过 然后遍历四个方向 用x,y分别记录坐标 判断坐标是否越界 然后进入dfs下一次搜索
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void dfs(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // 终止条件:访问过的节点 或者 遇到海水visited[x][y] = true; // 标记访问过for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = x + dir[i][0];int nexty = y + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);}
}int result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true}}}bfs
bfs是要把当前节点所连接的节点都要遍历一遍 再进行下一步 所以我们也可以用到队列 只要元素加入队列 我们就标记为访问过 然后当队列不为空的时候 我们取出队列里面的元素 就是当前所遍历的元素 然后遍历四个方向 判断边界是否越界 如果这四个方向的节点有没有访问过的陆地 就把它们加入队列 然后标记
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void bfs(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {queue<pair<int, int>> que;que.push({x, y});visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记while(!que.empty()) {pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();int curx = cur.first;int cury = cur.second;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) {que.push({nextx, nexty});visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记}}}
}100. 岛屿的最大面积
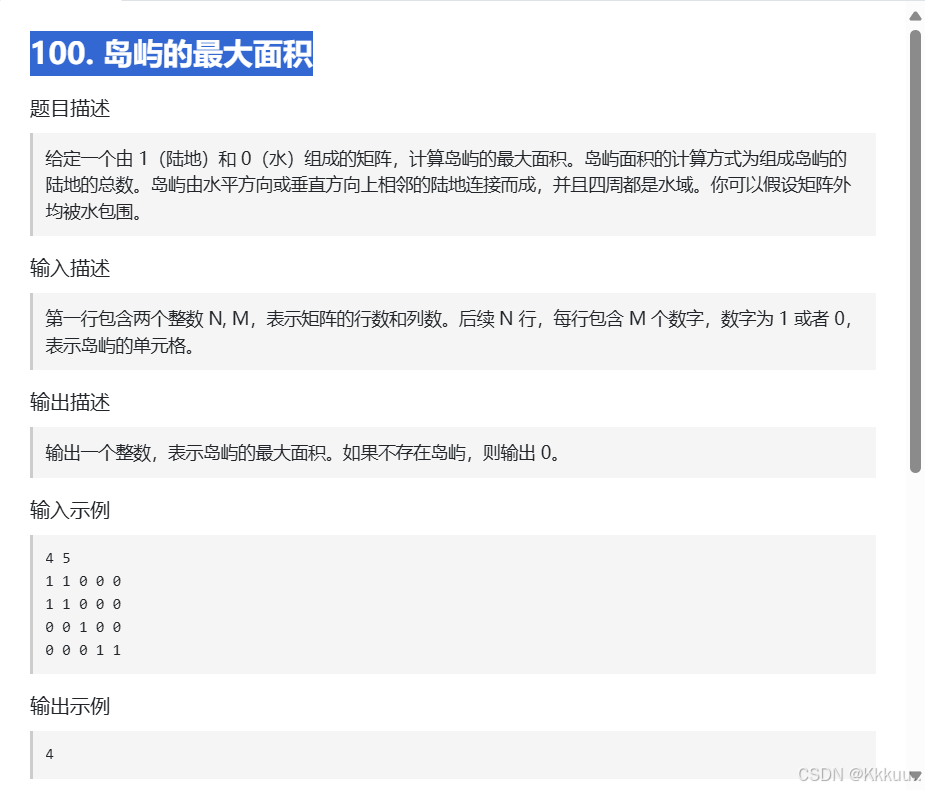
这一题是求所有岛屿中最大的岛屿面积
dfs
我们就用一个count记录当前岛屿的面积 然后每当我们在主函数遇到一个没有访问过的陆地 我们就归零count然后进入dfs深搜 在dfs逻辑里面 标记一个地点就count++
int count;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // 终止条件:访问过的节点 或者 遇到海水visited[x][y] = true; // 标记访问过count++;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = x + dir[i][0];int nexty = y + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);}
}bfs
同dfs一样的思路 代码不一样 创建队列的时候 可以用pair 也可以分别把x,y都放进队列里
int count;int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {queue<int> que;que.push(x);que.push(y);visited[x][y] = true; // 加入队列就意味节点是陆地可到达的点count++;while(!que.empty()) {int xx = que.front();que.pop();int yy = que.front();que.pop();for (int i = 0 ;i < 4; i++) {int nextx = xx + dir[i][0];int nexty = yy + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) { // 节点没有被访问过且是陆地visited[nextx][nexty] = true;count++;que.push(nextx);que.push(nexty);}}}}101. 孤岛的总面积
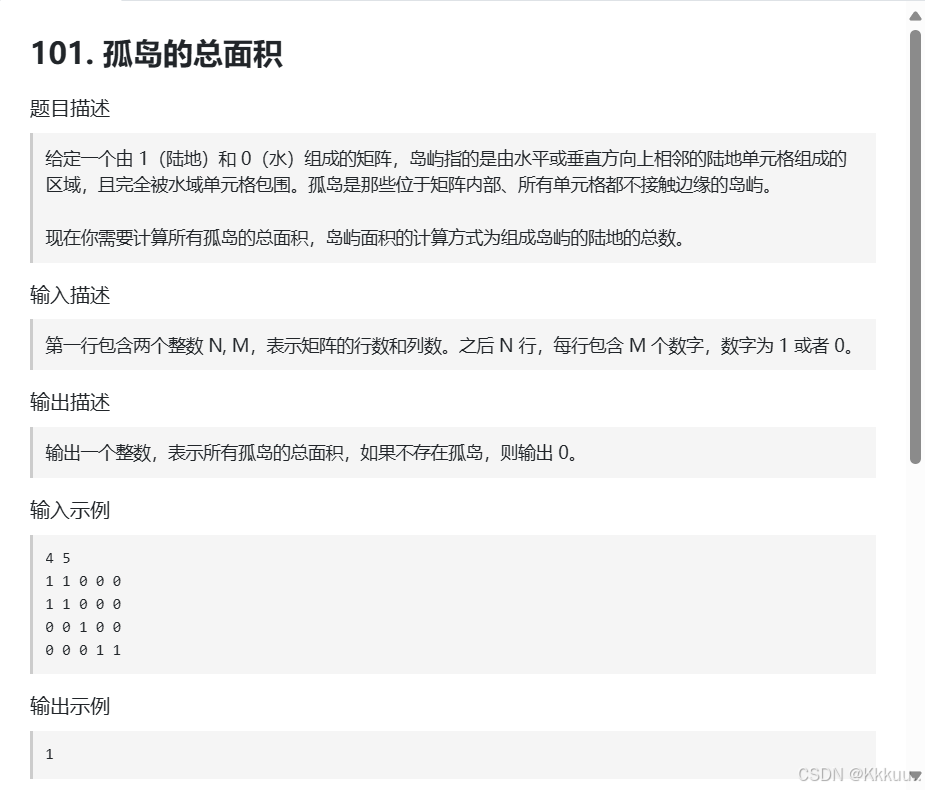
本题是求孤岛的总面积 孤岛就是陆地不接触边缘的岛屿 我们可以用一个思路从四个边缘开始搜索 只要遇到陆地就把它变成水域 最后剩下的岛屿就是孤岛
dfs
优化:如果四个方向中有水域就不用继续深搜下去
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int dir[4][2] = {-1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0, 1}; // 保存四个方向
int count; // 统计符合题目要求的陆地空格数量
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int x, int y) {grid[x][y] = 0;count++;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 向四个方向遍历int nextx = x + dir[i][0];int nexty = y + dir[i][1];// 超过边界if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue;// 不符合条件,不继续遍历if (grid[nextx][nexty] == 0) continue;dfs (grid, nextx, nexty);}return;
}int main() {int n, m;cin >> n >> m;vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(m, 0));for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {cin >> grid[i][j];}}// 从左侧边,和右侧边 向中间遍历for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (grid[i][0] == 1) dfs(grid, i, 0);if (grid[i][m - 1] == 1) dfs(grid, i, m - 1);}// 从上边和下边 向中间遍历for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (grid[0][j] == 1) dfs(grid, 0, j);if (grid[n - 1][j] == 1) dfs(grid, n - 1, j);}count = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (grid[i][j] == 1) dfs(grid, i, j);}}cout << count << endl;
}bfs
int count = 0;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int x, int y) {queue<pair<int, int>> que;que.push({x, y});grid[x][y] = 0; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记count++;while(!que.empty()) {pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();int curx = cur.first;int cury = cur.second;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过if (grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) {que.push({nextx, nexty});count++;grid[nextx][nexty] = 0; // 只要加入队列立刻标记}}}
}102. 沉没孤岛

本题要求我们把孤岛变成0 其实这一题和上一题求孤岛思路差不多 我们同样是先从边缘开始搜索 遇到陆地我们可以赋值为2 然后最后两层for'循环将2赋值成1 将剩下的孤岛1赋值成0
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int dir[4][2] = {-1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0, 1}; // 保存四个方向
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int x, int y) {grid[x][y] = 2;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 向四个方向遍历int nextx = x + dir[i][0];int nexty = y + dir[i][1];// 超过边界if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue;// 不符合条件,不继续遍历if (grid[nextx][nexty] == 0 || grid[nextx][nexty] == 2) continue;dfs (grid, nextx, nexty);}return;
}int main() {int n, m;cin >> n >> m;vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(m, 0));for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {cin >> grid[i][j];}}// 步骤一:// 从左侧边,和右侧边 向中间遍历for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (grid[i][0] == 1) dfs(grid, i, 0);if (grid[i][m - 1] == 1) dfs(grid, i, m - 1);}// 从上边和下边 向中间遍历for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (grid[0][j] == 1) dfs(grid, 0, j);if (grid[n - 1][j] == 1) dfs(grid, n - 1, j);}// 步骤二、步骤三for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (grid[i][j] == 1) grid[i][j] = 0;if (grid[i][j] == 2) grid[i][j] = 1;}}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {cout << grid[i][j] << " ";}cout << endl;}
}






