一、tracepoint 的机制
1.1 DECLARE_HOOK 解析
DECLARE_HOOK(vendor_bond_check_dev_link,TP_PROTO(const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state), TP_ARGS(bond, slave, state));
// 在已经实现如下宏定义的前提下
// CONFIG_TRACEPOINTS 和 CONFIG_VENDOR_HOOKS
#include <trace/hooks/vendor_hooks.h> // 没有的化自行添加
#define DECLARE_HOOK DECLARE_TRACE#include <linux/tracepoint.h>
#define DECLARE_TRACE(name, proto, args) \__DECLARE_TRACE(name, PARAMS(proto), PARAMS(args), \cpu_online(raw_smp_processor_id()), \PARAMS(void *__data, proto))#define PARAMS(args...) args
#define TP_PROTO(args...) args
#define TP_ARGS(args...) args
经过转换后
__DECLARE_TRACE(vendor_bond_check_dev_link, PARAMS(const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state), PARAMS(bond, slave, state), \cpu_online(raw_smp_processor_id()), \PARAMS(void *__data, const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state))|||||||||||||||\|||/\|/|
__DECLARE_TRACE(vendor_bond_check_dev_link, \PARAMS(const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state), \PARAMS(bond, slave, state), \cpu_online(raw_smp_processor_id()), \PARAMS(void *__data, const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state))
进一步解析
#define raw_smp_processor_id() (current_thread_info()->cpu) // 获取运行当前线程的CPUID
#define cpu_online(cpu) cpumask_test_cpu((cpu), cpu_online_mask) // 测试 CPU 掩码中的 CPU
#define __DECLARE_TRACE(name, proto, args, cond, data_proto) \extern int __traceiter_##name(data_proto); \DECLARE_STATIC_CALL(tp_func_##name, __traceiter_##name); \extern struct tracepoint __tracepoint_##name; \static inline void trace_##name(proto) \{ \if (static_key_false(&__tracepoint_##name.key)) \__DO_TRACE(name, \TP_ARGS(args), \TP_CONDITION(cond), 0); \if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_LOCKDEP) && (cond)) { \rcu_read_lock_sched_notrace(); \rcu_dereference_sched(__tracepoint_##name.funcs); \rcu_read_unlock_sched_notrace(); \} \} \__DECLARE_TRACE_RCU(name, PARAMS(proto), PARAMS(args), \PARAMS(cond)) \static inline int \register_trace_##name(void (*probe)(data_proto), void *data) \{ \return tracepoint_probe_register(&__tracepoint_##name, \(void *)probe, data); \} \static inline int \register_trace_prio_##name(void (*probe)(data_proto), void *data, \int prio) \{ \return tracepoint_probe_register_prio(&__tracepoint_##name, \(void *)probe, data, prio); \} \static inline int \unregister_trace_##name(void (*probe)(data_proto), void *data) \{ \return tracepoint_probe_unregister(&__tracepoint_##name, \(void *)probe, data); \} \static inline void \check_trace_callback_type_##name(void (*cb)(data_proto)) \{ \} \static inline bool \trace_##name##_enabled(void) \{ \return static_key_false(&__tracepoint_##name.key); \}
转换后结果
__DECLARE_TRACE( \vendor_bond_check_dev_link, \PARAMS(const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state), \PARAMS(bond, slave, state), \cpu_online(raw_smp_processor_id()), \PARAMS(void *__data, const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state) \
)|||||||||||||||\|||/\|/|
extern int __traceiter_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(void *__data, const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state);
DECLARE_STATIC_CALL(tp_func_vendor_bond_check_dev_link, __traceiter_vendor_bond_check_dev_link);
extern struct tracepoint __tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link;static inline void trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state)
{if (static_key_false(&__tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link.key))__DO_TRACE(vendor_bond_check_dev_link,TP_ARGS(bond, slave, state),TP_CONDITION(cpu_online(raw_smp_processor_id())), 0);if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_LOCKDEP) && (cpu_online(raw_smp_processor_id()))) {rcu_read_lock_sched_notrace();rcu_dereference_sched(__tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link.funcs);rcu_read_unlock_sched_notrace();}
}__DECLARE_TRACE_RCU( \vendor_bond_check_dev_link, \PARAMS(const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state), \PARAMS(bond, slave, state), \PARAMS(cpu_online(raw_smp_processor_id()))
)static inline int register_trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(void (*probe)(void *__data, const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state),void *data)
{return tracepoint_probe_register(&__tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link, (void *)probe, data);
}static inline int register_trace_prio_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(void (*probe)(void *__data, const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state),void *data, int prio)
{return tracepoint_probe_register_prio(&__tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link, (void *)probe, data, prio);
}static inline int unregister_trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(void (*probe)(void *__data, const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state),void *data)
{return tracepoint_probe_unregister(&__tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link, (void *)probe, data);
}static inline void check_trace_callback_type_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(void (*cb)(void *__data, const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state))
{
}static inline bool trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link_enabled(void)
{return static_key_false(&__tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link.key);
}
1.2 DECLARE_STATIC_CALL 解析
#define DECLARE_STATIC_CALL(name, func) \extern struct static_call_key STATIC_CALL_KEY(name); \extern typeof(func) STATIC_CALL_TRAMP(name);#define STATIC_CALL_KEY(name) __PASTE(STATIC_CALL_KEY_PREFIX, name)
#define __PASTE(a,b) ___PASTE(a,b)
#define ___PASTE(a,b) a##b
#define STATIC_CALL_KEY_PREFIX __SCK__#define STATIC_CALL_TRAMP(name) __PASTE(STATIC_CALL_TRAMP_PREFIX, name)
#define STATIC_CALL_TRAMP_PREFIX __SCT__|||||||||||||||\|||/\|/|
#define DECLARE_STATIC_CALL(name, func) \extern struct static_call_key __SCK__##name; \extern typeof(func) __SCT__##name;
转换后
extern int __traceiter_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(void *__data, const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state);
DECLARE_STATIC_CALL(tp_func_vendor_bond_check_dev_link, __traceiter_vendor_bond_check_dev_link);|||||||||||||||\|||/\|/|
extern int __traceiter_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(void *__data, const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state);
extern struct static_call_key __SCK__tp_func_vendor_bond_check_dev_link;
extern typeof(__traceiter_vendor_bond_check_dev_link) __SCT__tp_func_vendor_bond_check_dev_link; // 定义一个和__traceiter_vendor_bond_check_dev_link相同类型的变量
1.3 trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link 函数解析---执行钩子函数
struct tracepoint {const char *name;struct static_key key;struct static_call_key *static_call_key;void *static_call_tramp;void *iterator;int (*regfunc)(void);void (*unregfunc)(void);struct tracepoint_func __rcu *funcs;
};extern struct tracepoint __tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link;static inline void trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state)
{// 使用了全局变量__tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link,必定有地方会初始化了该变量if (static_key_false(&__tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link.key))__DO_TRACE(vendor_bond_check_dev_link,TP_ARGS(bond, slave, state),TP_CONDITION(cpu_online(raw_smp_processor_id())), 0);if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_LOCKDEP) && (cpu_online(raw_smp_processor_id()))) {rcu_read_lock_sched_notrace();rcu_dereference_sched(__tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link.funcs);rcu_read_unlock_sched_notrace();}
}
1.4 __DECLARE_TRACE_RCU 解析
#define __DECLARE_TRACE_RCU(name, proto, args, cond) \static inline void trace_##name##_rcuidle(proto) \{ \if (static_key_false(&__tracepoint_##name.key)) \__DO_TRACE(name, \TP_ARGS(args), \TP_CONDITION(cond), 1); \}
1.5 register_trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link 函数介绍---注册钩子函数
static inline int register_trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(void (*probe)(void *__data, const struct bonding *bond, const struct slave *slave, int *state),void *data)
{return tracepoint_probe_register(&__tracepoint_vendor_bond_check_dev_link, (void *)probe, data);
}
int tracepoint_probe_register(struct tracepoint *tp, void *probe, void *data)
{return tracepoint_probe_register_prio(tp, probe, data, TRACEPOINT_DEFAULT_PRIO);
}
int tracepoint_probe_register_prio(struct tracepoint *tp, void *probe, void *data, int prio)
{struct tracepoint_func tp_func;int ret;mutex_lock(&tracepoints_mutex);tp_func.func = probe;tp_func.data = data;tp_func.prio = prio;ret = tracepoint_add_func(tp, &tp_func, prio, true); // 整个过程就是显示tp = tp_funcmutex_unlock(&tracepoints_mutex);return ret;
}
static int tracepoint_add_func(struct tracepoint *tp,struct tracepoint_func *func, int prio, bool warn)
{struct tracepoint_func *old, *tp_funcs;int ret;if (tp->regfunc && !static_key_enabled(&tp->key)) {ret = tp->regfunc();if (ret < 0)return ret;}// 核心代码1,拿到钩子列表tp_funcs = rcu_dereference_protected(tp->funcs,lockdep_is_held(&tracepoints_mutex));// 核心代码2,注册新的钩子到列表old = func_add(&tp_funcs, func, prio);if (IS_ERR(old)) {WARN_ON_ONCE(warn && PTR_ERR(old) != -ENOMEM);return PTR_ERR(old);}/** rcu_assign_pointer has as smp_store_release() which makes sure* that the new probe callbacks array is consistent before setting* a pointer to it. This array is referenced by __DO_TRACE from* include/linux/tracepoint.h using rcu_dereference_sched().*/switch (nr_func_state(tp_funcs)) {case TP_FUNC_1: /* 0->1 *//** Make sure new static func never uses old data after a* 1->0->1 transition sequence.*/tp_rcu_cond_sync(TP_TRANSITION_SYNC_1_0_1);/* Set static call to first function */tracepoint_update_call(tp, tp_funcs);/* Both iterator and static call handle NULL tp->funcs */rcu_assign_pointer(tp->funcs, tp_funcs);static_key_enable(&tp->key);break;case TP_FUNC_2: /* 1->2 *//* Set iterator static call */tracepoint_update_call(tp, tp_funcs);/** Iterator callback installed before updating tp->funcs.* Requires ordering between RCU assign/dereference and* static call update/call.*/fallthrough;case TP_FUNC_N: /* N->N+1 (N>1) */rcu_assign_pointer(tp->funcs, tp_funcs);/** Make sure static func never uses incorrect data after a* N->...->2->1 (N>1) transition sequence.*/if (tp_funcs[0].data != old[0].data)tp_rcu_get_state(TP_TRANSITION_SYNC_N_2_1);break;default:WARN_ON_ONCE(1);break;}release_probes(old);return 0;
}
1.6 unregister_trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link 函数解析---注销钩子函数
不做介绍了,和 register 类似
二、tracepiont 其他的功能介绍
【待补充】
三、Demo 实例讲解
后面实现用例的时候补充,当前仅介绍官方的 demo
3.1 驱动侧代码实现
#include <trace/hooks/bonding.h>static void vendor_foo(void *data, const struct bonding *bond,const struct slave *slave, int *state)
{pr_info("%s\n", __func__);
}static int __init vendor_bond_init(void)
{return register_trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(&vendor_foo, NULL);
}static void __exit vendor_bond_exit(void)
{unregister_trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(&vendor_foo, NULL);
}module_init(vendor_bond_init);
module_exit(vendor_bond_exit);
3.2 内核侧代码实现
代码合入链接
3.3 测试代码
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <net/bonding.h>
#include <trace/hooks/bonding.h>static void vendor_bond_check_dev_link(void *data, const struct bonding *bond,const struct slave *slave, int *state)
{pr_info("%s\n", __func__);
}static int __init bondingTestInit(void)
{return register_trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(&vendor_bond_check_dev_link, NULL);
}static void __exit bondingTestExit(void)
{printk("bonding test exit\n");unregister_trace_vendor_bond_check_dev_link(&vendor_bond_check_dev_link, NULL);
}/* 模块入口和出口函数 */
module_init(bondingTestInit)
module_exit(bondingTestExit)/* 模块信息 */
MODULE_AUTHOR("Wei Yongjun <[email]weiyongjun1@huawei.com[/email]>");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_ESCRIPTION("bondtest driver");最后
有很多小伙伴不知道学习哪些鸿蒙开发技术?不知道需要重点掌握哪些鸿蒙应用开发知识点?而且学习时频繁踩坑,最终浪费大量时间。所以有一份实用的鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)资料用来跟着学习是非常有必要的。
鸿蒙HarmonyOS Next全套学习资料←点击领取!(安全链接,放心点击)
这份鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)资料包含了鸿蒙开发必掌握的核心知识要点,内容包含了(ArkTS、ArkUI开发组件、Stage模型、多端部署、分布式应用开发、音频、视频、WebGL、OpenHarmony多媒体技术、Napi组件、OpenHarmony内核、Harmony南向开发、鸿蒙项目实战等等)鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)技术知识点。
希望这一份鸿蒙学习资料能够给大家带来帮助,有需要的小伙伴自行领取,限时开源,先到先得~无套路领取!!
鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)最新学习路线
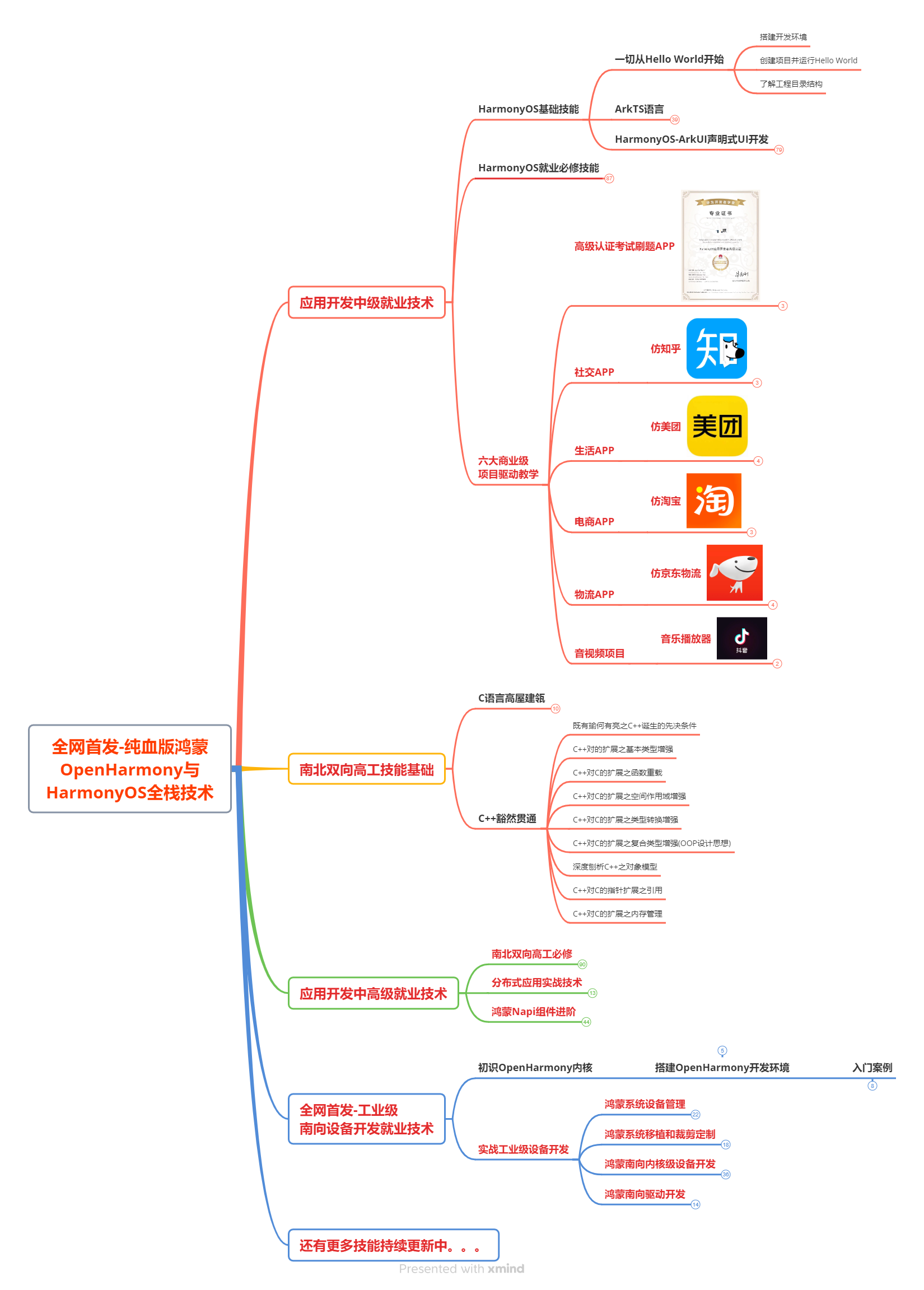
有了路线图,怎么能没有学习资料呢,小编也准备了一份联合鸿蒙官方发布笔记整理收纳的一套系统性的鸿蒙(OpenHarmony )学习手册(共计1236页)与鸿蒙(OpenHarmony )开发入门教学视频,内容包含:ArkTS、ArkUI、Web开发、应用模型、资源分类…等知识点。
获取以上完整版高清学习路线,请点击→纯血版全套鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料
HarmonyOS Next 最新全套视频教程
《鸿蒙 (OpenHarmony)开发基础到实战手册》
OpenHarmony北向、南向开发环境搭建
《鸿蒙开发基础》
- ArkTS语言
- 安装DevEco Studio
- 运用你的第一个ArkTS应用
- ArkUI声明式UI开发
- .……

《鸿蒙开发进阶》
- Stage模型入门
- 网络管理
- 数据管理
- 电话服务
- 分布式应用开发
- 通知与窗口管理
- 多媒体技术
- 安全技能
- 任务管理
- WebGL
- 国际化开发
- 应用测试
- DFX面向未来设计
- 鸿蒙系统移植和裁剪定制
- ……

《鸿蒙进阶实战》
- ArkTS实践
- UIAbility应用
- 网络案例
- ……

大厂面试必问面试题

鸿蒙南向开发技术
鸿蒙APP开发必备

鸿蒙生态应用开发白皮书V2.0PDF

获取以上完整鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料,请点击→
纯血版全套鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料
总结
总的来说,华为鸿蒙不再兼容安卓,对中年程序员来说是一个挑战,也是一个机会。只有积极应对变化,不断学习和提升自己,他们才能在这个变革的时代中立于不败之地。



)


