一、链表的概念和结构
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的,在逻辑上连续,物理内存上不连续
链表的形式有很多,我们主要掌握两种:
- 无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据,实际中更多的是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等,另外这种结构在笔试面试中会出现很多
- 无头双向链表:在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向链表
二、无头单向非循环链表的实现
1. 定义一个链表
public class MySingleList {static class ListNode {public ListNode next;//下一个节点的地址public int val;//节点的值域public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}public ListNode head;//表示当前链表的头节点}
2. 创建节点
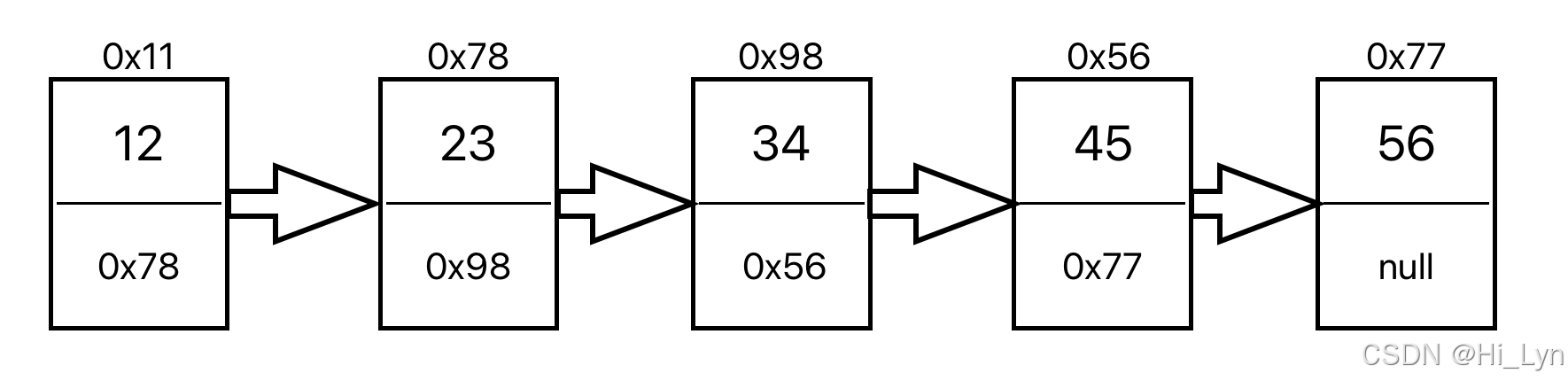
public void creatList(){ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);ListNode node2 = new ListNode(23);ListNode node3 = new ListNode(34);ListNode node4 = new ListNode(45);ListNode node5 = new ListNode(56);
这样之后我们只创建了单独的数据,如图所示

3.形成链表
node1.next = node2;node2.next = node3;node3.next = node4;node4.next = node5;this.head = node1;
三、无头单向非循环链表的几种方法
1.打印元素
定义一个cur相当于head,如果cur不等于空,那么就打印对应的内容
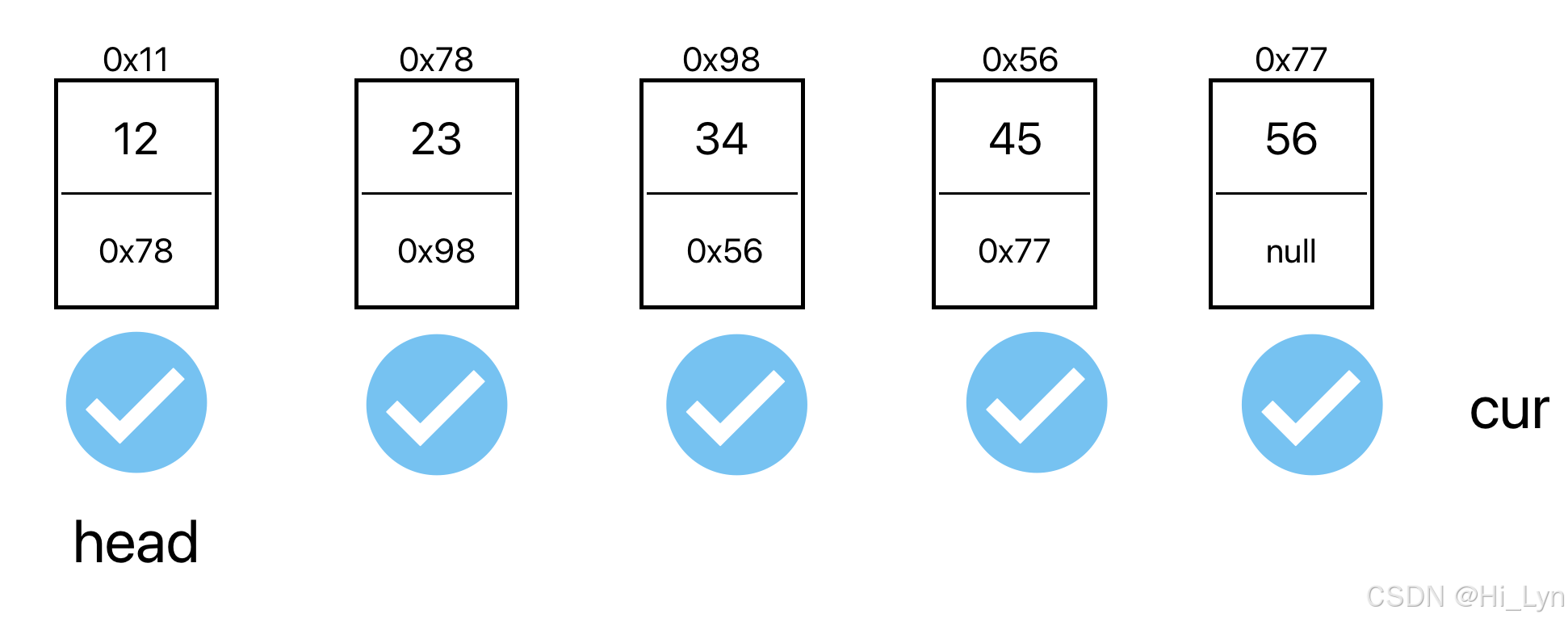
public void display(){ListNodes cur = head;while (cur != null){System.out.print(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}
//输出结果
12 23 34 45 56 Process finished with exit code 0
2.头插法
在head的前面插入一个元素,注意,在插入的的时候先绑定后面的节点信息
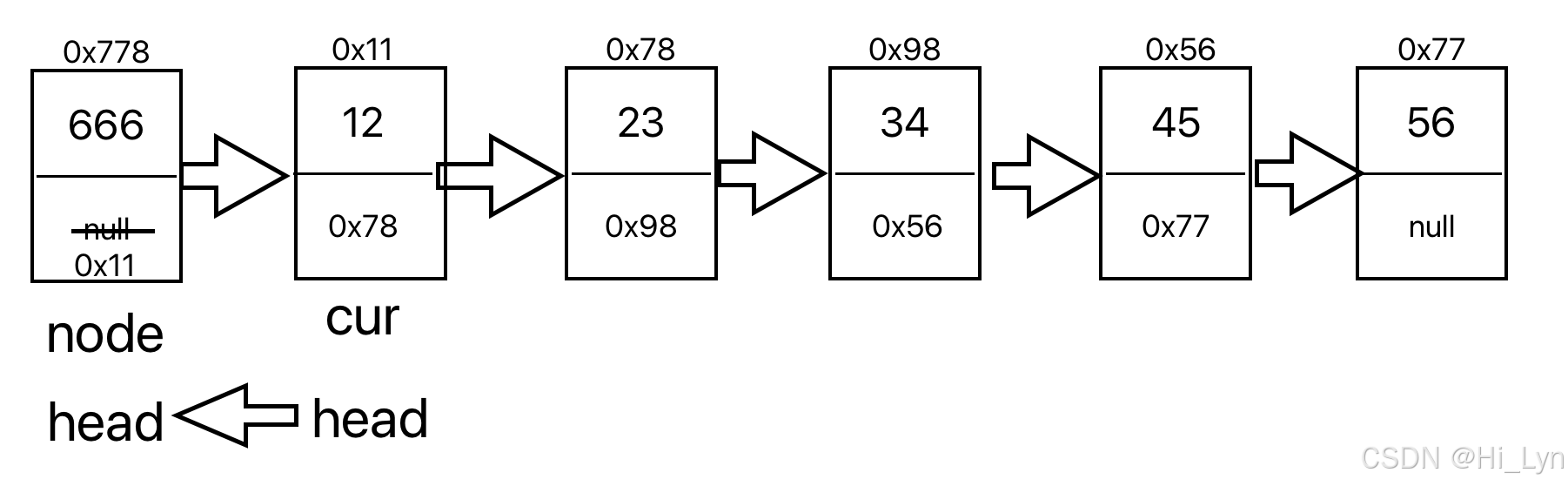
public void addFirst(int data){ListNodes nodes = new ListNodes(data);nodes.next = head;head = nodes;}
//输出结果
666 12 23 34 45 56 Process finished with exit code 0
3.尾插法
当cur.next==null时说明整个链表遍历完成了,cur所指向的节点就是尾巴节点,是最后一个节点的位置
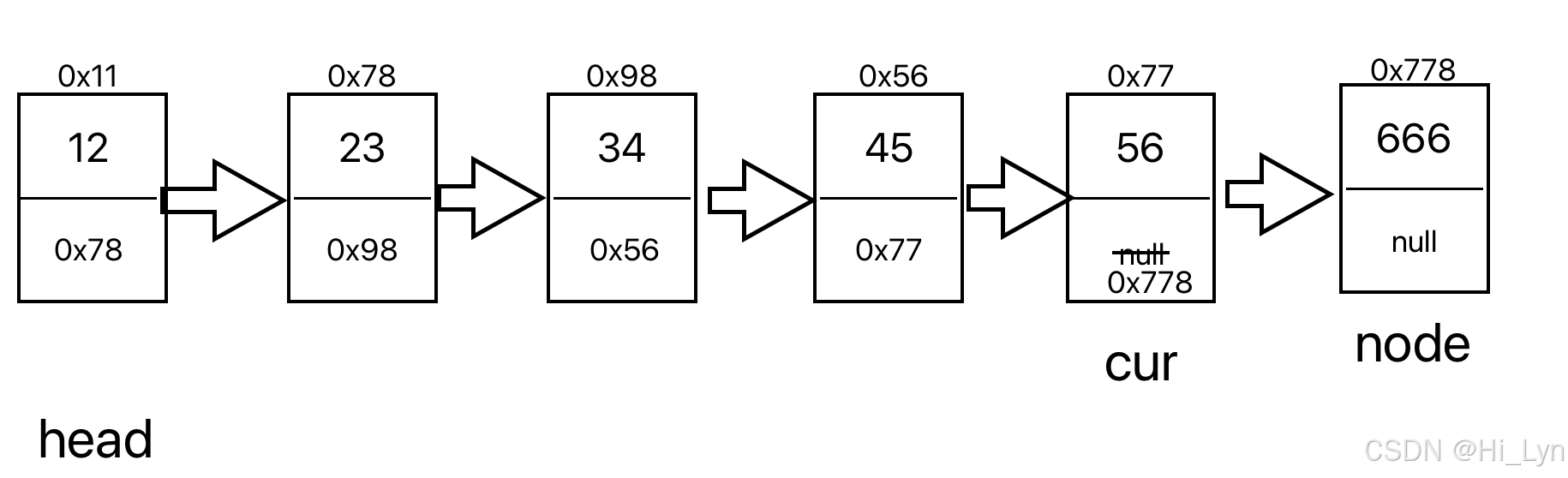
public void addLast(int data){ListNodes nodes = new ListNodes(data);ListNodes cur = head;if (cur == null){head = nodes;return;}while (cur.next != null){cur = cur.next;}cur.next = nodes;}
//输出结果
12 23 34 45 56 666 Process finished with exit code 0
4.得到单链表的长度
public int size(){ListNodes cur = head;int count = 0;while (cur != null){count++;cur = cur.next;}return count;}
//输出结果
7Process finished with exit code 0
5.任意位置插入
需要判断是否为第一个和最后一个节点然后再进行插入
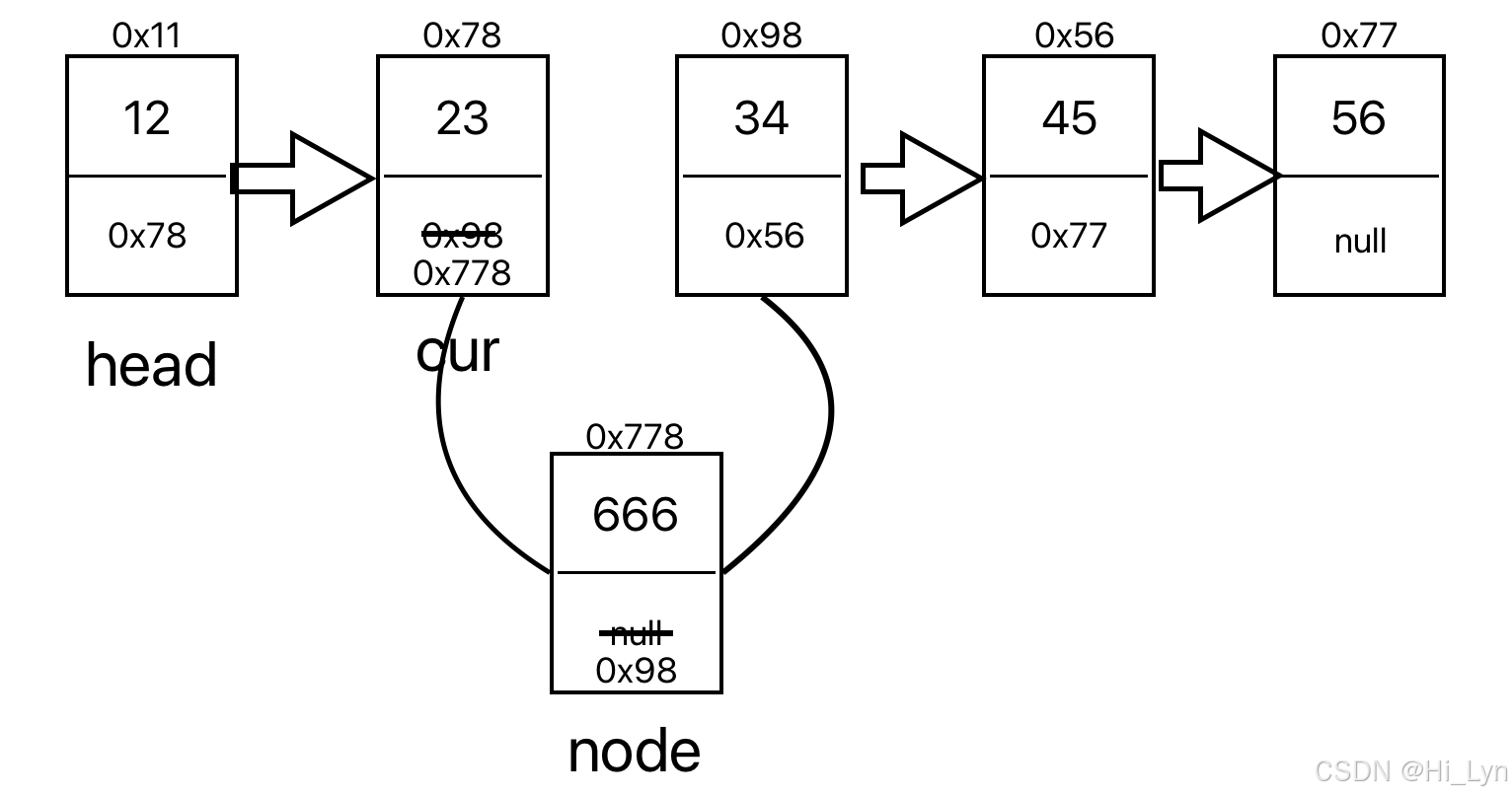
public ListNodes findnodeSubone(int index){ListNodes cur = head;while (index -1 != 0){cur = cur.next;index--;}return cur;}public void addIndex(int index,int data){if (index < 0 || index > size()){System.out.println("位置不合法!");}if (index == 0 ){addFirst(data);return;}if (index == size()){addLast(data);return;}ListNodes cur = findnodeSubone(index);ListNodes nodes = new ListNodes(data);nodes.next = cur.next;cur.next = nodes;}
//运行结果
666 12 23 666 34 45 56 666 Process finished with exit code 0
6.查找是否包含关键字key在单链表中
public boolean contains(int key){ListNodes cur = head;while (cur != null){if (cur.val == key){return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}
//运行结果
trueProcess finished with exit code 0
7.删除第一次出现关键字key的节点
public ListNodes Search(int key){ListNodes cur = head;while (cur.next != null){if (cur.next.val == key){return cur;}cur = cur.next;}return null;}public void remove(int key){if (head == null){return;}if (head.val == key){head = head.next;return;}ListNodes cur = Search(key);if (cur ==null){System.out.println("没有要删除的数字");return;}ListNodes del = cur.next;cur.next = del.next;}
//输出结果
12 23 666 34 45 56 666 Process finished with exit code 0
8.删除所有值为key的节点
cur代表当前要删除的节点,prev代表要删除节点的前驱
public void removeAll(int key){ListNodes cur = head;ListNodes prev = Search(key);if (head == null){return;}while (cur != null){if (cur.val == key){prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;}else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}if (head.val == key){head = head.next;}}//输出结果
12 23 34 45 56 Process finished with exit code 0
9.清空单链表
只需让头节点为空即可
public void clean(){this.head = null;}
//输出结果Process finished with exit code 0
四、无头双向链表的模拟实现
1.头插法
public void addFirst(int val){ListNode next;ListNode prev;ListNode node = new ListNode(val);if (head != null){node.next = head;head.prev = node;head = node;}else {head = node;last = node;}}
2.尾插法
public void addLast(int val){ListNode node = new ListNode(val);if (head == null){head = node;last = node;}else {last.next = node;node.prev = last;last = last.next;}}
3.任意位置插入
public ListNode search(int index){ListNode cur = head;while (index != 0){cur = cur.next;index--;}return cur;}public void addIndex(int data,int index){if (index < 0 || index > size()){//throw new no("位置不合法");}if (index == 0){addFirst(data);}if (index == size()){addLast(data);}ListNode cur = search(index);ListNode node = new ListNode(data);node.next = cur;cur.prev .next = node;node.prev = cur.prev;cur.prev = node;}
4.删除第一次出现关键字key的节点
public void remove(int key){ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null){if (cur.val == key){if (cur == head){//删除头节点head = head.next;if (head != null){//考虑只有一个节点的情况下head.prev = null;}else {last =null;}}else {//删除中间节点和尾巴节点if (cur.next != null){cur.prev.next = cur.next;cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}else {cur.prev.next = cur.next;last = last.prev;}}return;}else {cur = cur.next;}}}
5.删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAll(int key){ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null){if (cur.val == key){if (cur == head){//删除头节点head = head.next;if (head != null){//考虑只有一个节点的情况下head.prev = null;}else {last =null;}}else {//删除中间节点和尾巴节点if (cur.next != null){cur.prev.next = cur.next;cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}else {cur.prev.next = cur.next;last = last.prev;}}cur = cur.next;}else {cur = cur.next;}}}
6.清除链表
public void clear(){ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null){ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.prev = null;cur.next = null;cur = curNext;}head = null;last = null;}
五、LinkedList
什么是LinkedList?
LinkedList的底层是双向链表结构,由于链表没有将元素存储在连续的空间中,元素存储在单独节点中,然后通过引用将节点链接起来了,因此在任意位置插入或者删除元素时,不需要搬移元素,效率比较高
1.LinkedList的使用
LinkedList的构造
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {//构造一个空的LinkedListList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();List<String> list1 = new LinkedList<>();list1.add("hello");list.add(666);System.out.println(list);System.out.println(list1);}
}
2.LinkedList的常用方法
3.ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
- ArrayList在物理上连续存储,LinkedList在逻辑上连续存储,在物理上不一定连续存储
- ArrayList头插效率低,插入需要扩容,LinkedList没有容量的概念
- 应用场景:ArrayList应用于元素高效存储+频繁访问,LinkedList适用于在任意位置插入和删除数据


、地图打印(webprinting)等服务)

——日期类和const成员函数)


