1.环境
语言:java
jdk版本:1.8
2.三种线程池场景使用
2.1 固定线程数执行,每个线程只执行1次,最后全部执行完毕后再进入最终方法处理收尾
public static void testEveryThreadFixedExecuteOne() {int threadNum = 4;ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadNum,threadNum, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(threadNum, () -> {//必须保证线程池的线程数与该类的值一致CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction)parties一致// 线程池线程执行cyclicBarrier.await()会减一并阻塞线程等待cyclicBarrier所有操作完为0则进入该方法。// 所有执行完毕,执行这里面操作。System.out.println("全部线程执行结束了,这里可以处理最后收尾的逻辑");});for (int curentPageNum = 1; curentPageNum <= threadNum; curentPageNum++) {int finalCurentPageNum = curentPageNum;threadPoolExecutor.execute(() -> {try {System.out.println("执行线程逻辑" + finalCurentPageNum);} catch (Exception exception) {exception.printStackTrace();} finally {try {cyclicBarrier.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});}//发送停止标志,线程全部执行完毕会直接关闭threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();}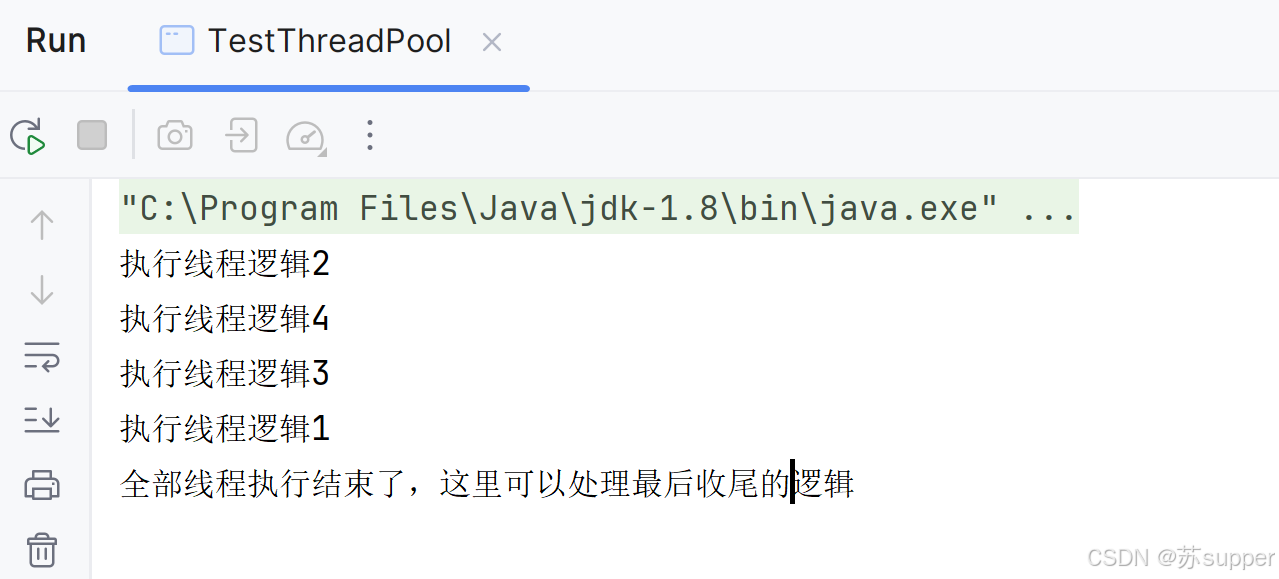
2.2 线程池的线程可被重复利用,直到所有任务都执行完成
public static void testThreadRepeatUse() {int threadNum = 4;int totalPageNum = 10;ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadNum,threadNum, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());for (int curentPageNum = 1; curentPageNum <= totalPageNum; curentPageNum++) {int finalCurentPageNum = curentPageNum;threadPoolExecutor.execute(() -> {System.out.println("执行" + finalCurentPageNum + " " + Thread.currentThread().getName());});}//发送停止标志,线程全部执行完毕会直接关闭threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();try {boolean awaitLoop = true;//阻塞判断do {awaitLoop = !threadPoolExecutor.awaitTermination(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);} while (awaitLoop);} catch (Exception exception) {exception.printStackTrace();threadPoolExecutor.shutdownNow();}System.out.println("线程都执行结束了,可以执行后续操作");}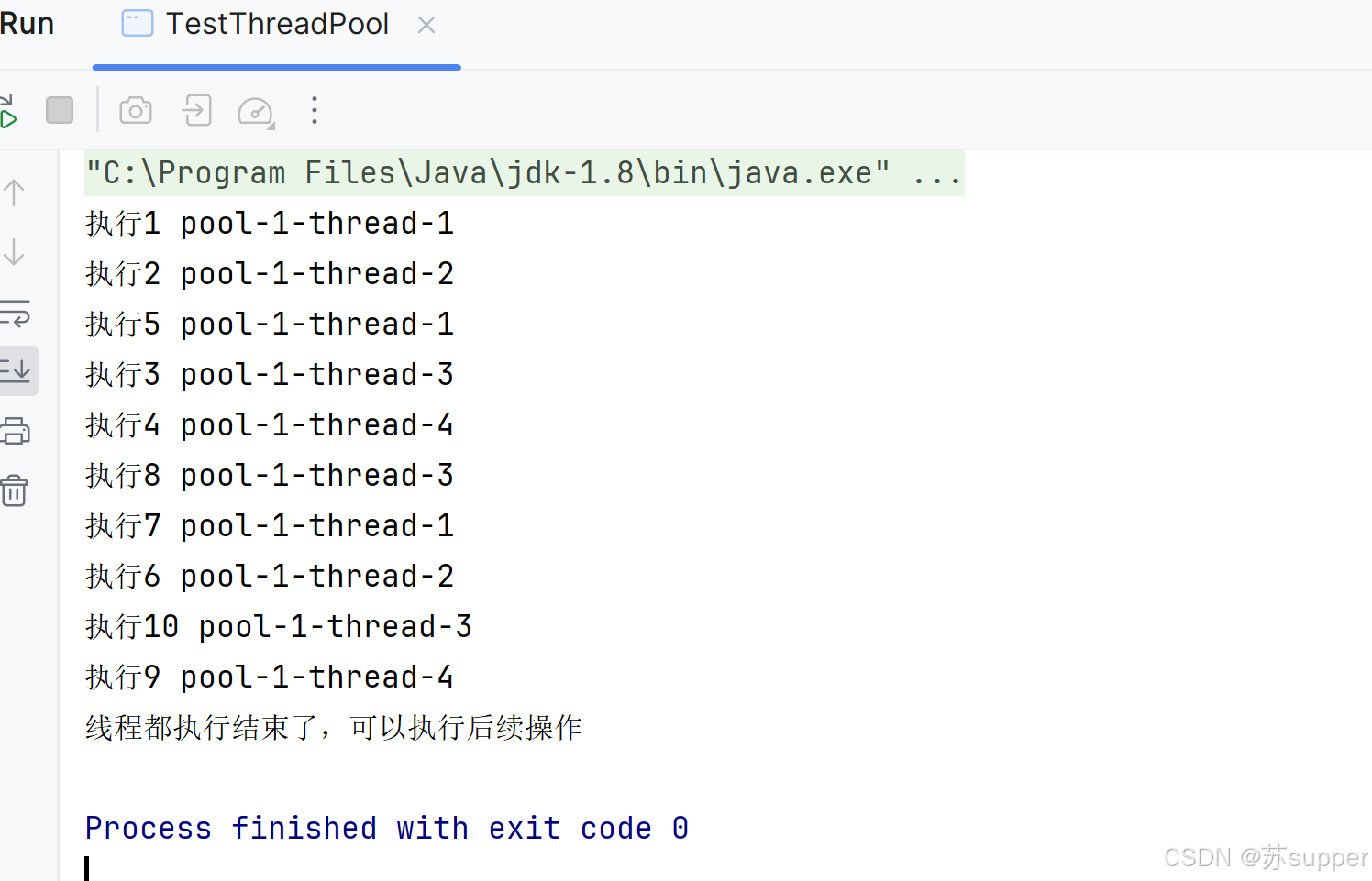
2.3 线程池的每个线程只执行一件事,最终得到所有线程的执行结果
public static void testGetAllThreadResult() throws Exception {int threadNum = 2;int execNum = 2;ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadNum,threadNum, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());List<Callable<List<Map<String, String>>>> callableList = new ArrayList<>();final AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0);for (int i = 0; i < execNum; i++) {callableList.add(new Callable<List<Map<String, String>>>() {@Overridepublic List<Map<String, String>> call() throws Exception {List<Map<String, String>> singleResultList = new ArrayList<>();int automicInt = atomicInteger.incrementAndGet();if (automicInt == 1) {System.out.println("我做第一件事,扫地");singleResultList = new ArrayList<>();LinkedHashMap<String, String> sweepMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();sweepMap.put("action", "sweep");singleResultList.add(sweepMap);} else if (automicInt == 2) {System.out.println("我做第二件事,擦玻璃");singleResultList = new ArrayList<>();LinkedHashMap<String, String> wipeMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();wipeMap.put("action", "wipe glass");singleResultList.add(wipeMap);}return singleResultList;}});}//这里会去调用执行并等待线程池内的所有任务执行完毕List<Future<List<Map<String, String>>>> futureList = threadPoolExecutor.invokeAll(callableList,7, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//全部执行完毕获取每个线程的返回值List<Map<String,String>> resultList =new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i <futureList.size() ; i++) {resultList.addAll(futureList.get(i).get());}System.out.println(String.format("全部执行完毕,结果集:%s",resultList));threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();}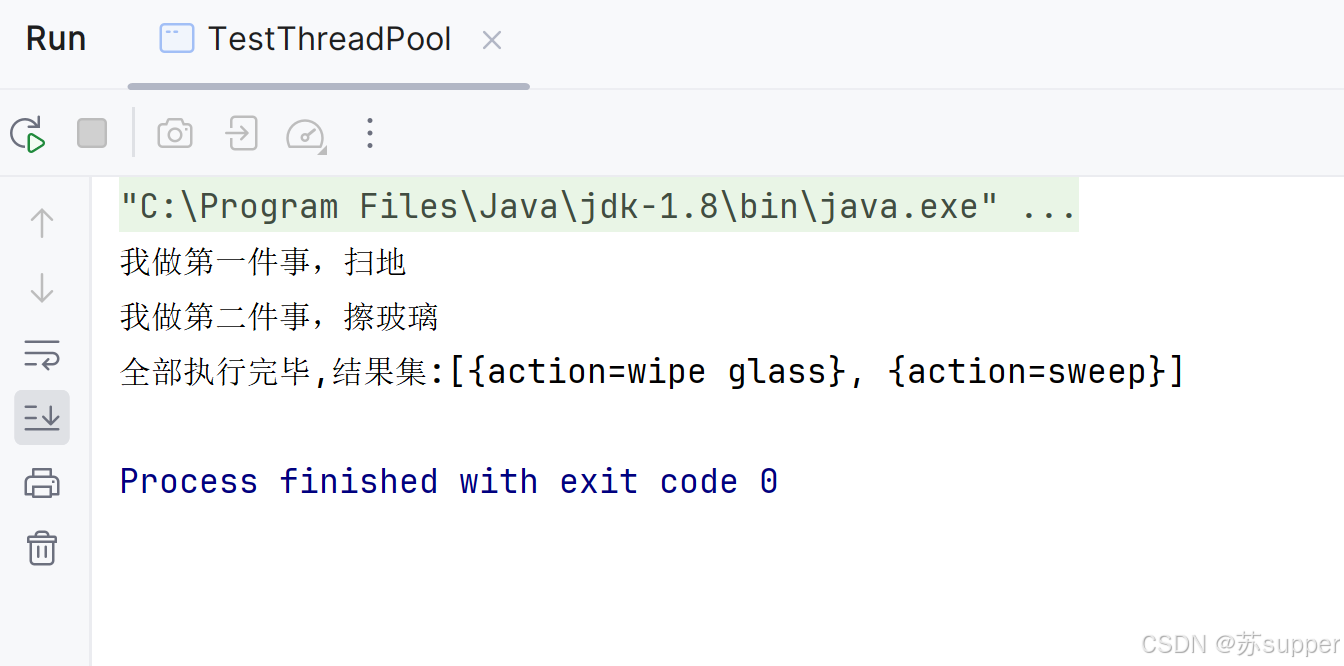
以上就是3种场景使用,可进行参考。



)


