目录
1.栈
1.1栈的概念及结构
1.2栈的实现
2.队列
2.1队列的概念及结构
2.2队列的实现
3.栈和队列经典题目
1.括号匹配问题
2. 用队列实现栈
1.栈
1.1栈的概念及结构
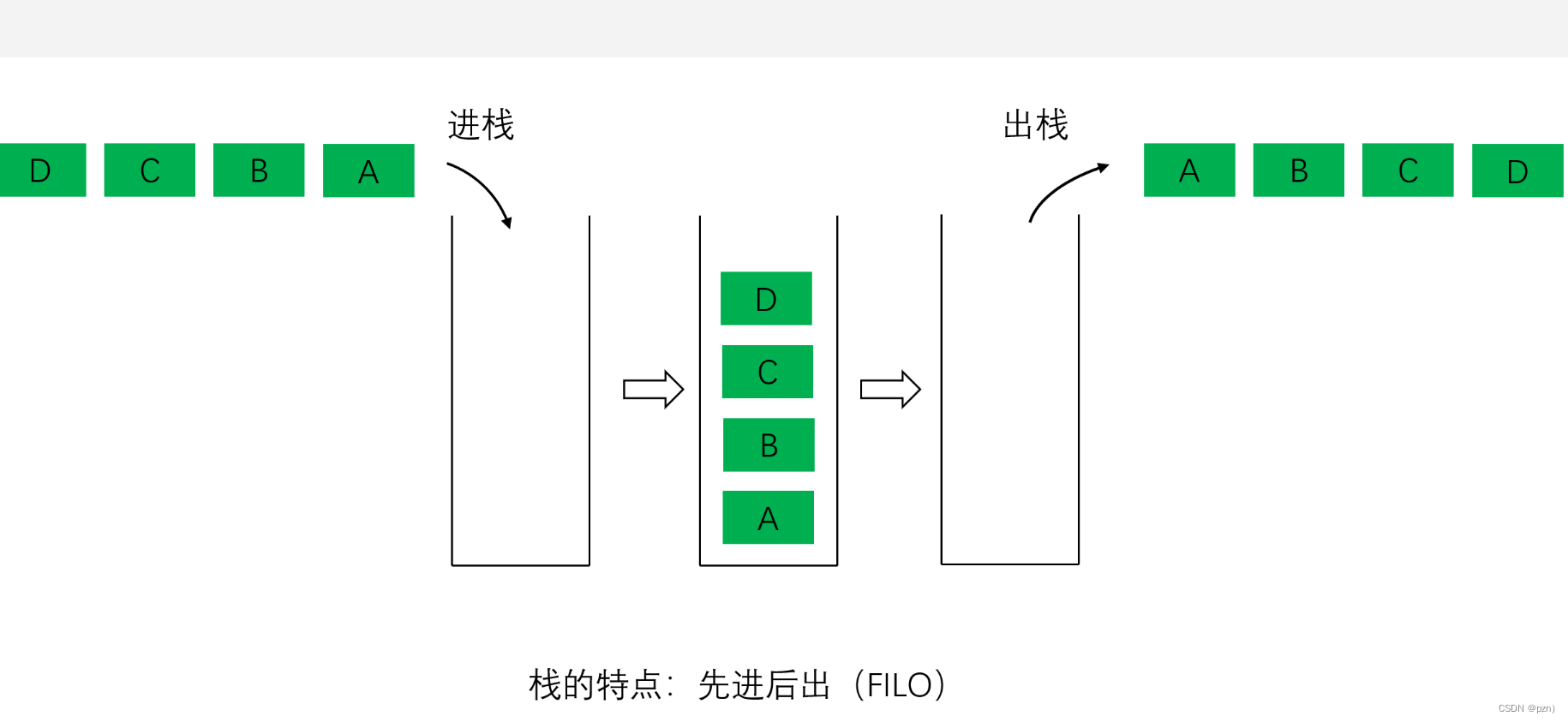
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。 进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为 栈顶 ,另一端称为 栈底 。 栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出 LIFO ( Last In First Out )的原则。压栈 :栈的插入操作叫做进栈 / 压栈 / 入栈, 入数据在栈顶 。出栈 :栈的删除操作叫做出栈。 出数据也在栈顶 。

1.2栈的实现
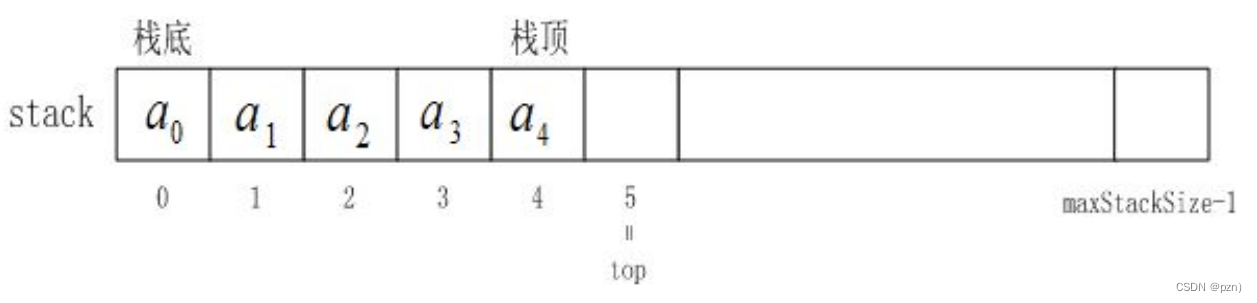
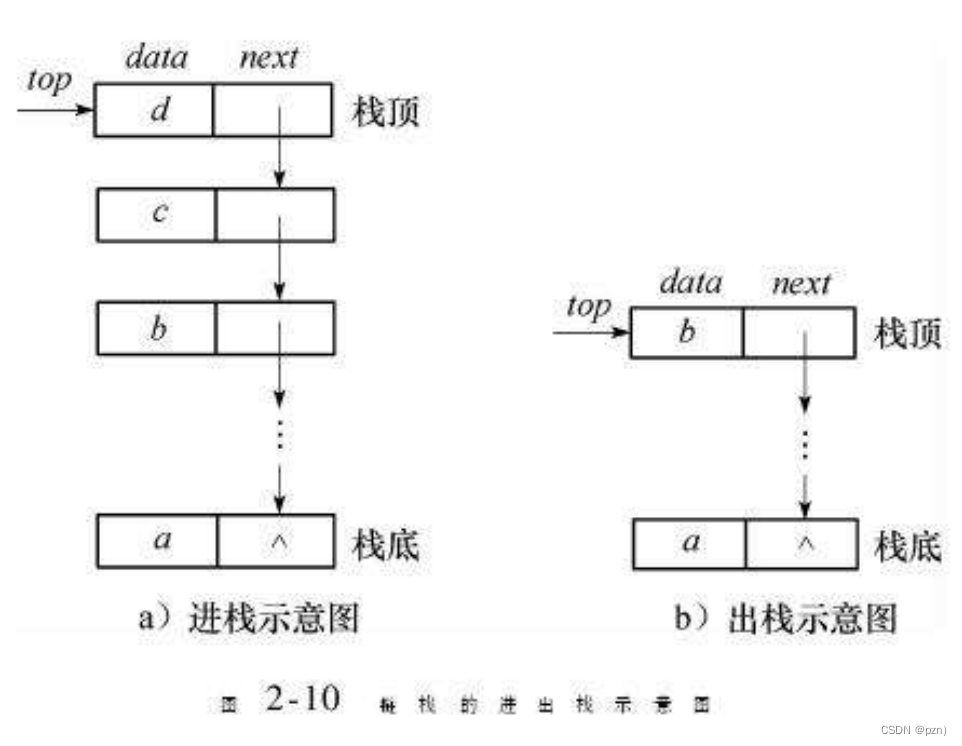
栈的实现一般可以使用 数组或者链表实现 ,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
#include"Queue.h"
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->phead;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
// 队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}newnode->next = NULL;newnode->val = x;if (pq->ptail == NULL){pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;}else{pq->ptail->next = newnode;pq->ptail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}// 队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->size != 0);//一个节点if (pq->phead->next == 0){free(pq->phead);pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;}//多个节点else{QNode* next = pq->phead->next;free(pq->phead);pq->phead = next;}pq->size--;
}// 取队头和队尾的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->phead);return pq->phead->val;
}QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->ptail);return pq->ptail->val;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size == 0;
}2.队列
2.1队列的概念及结构
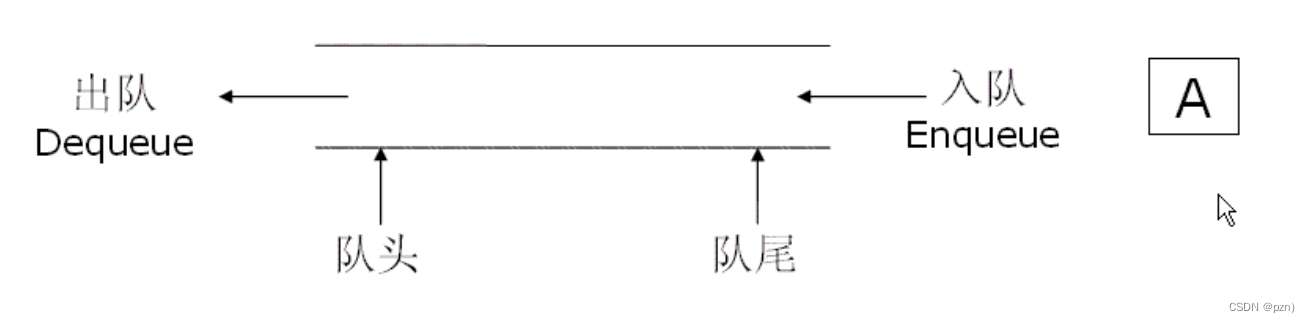
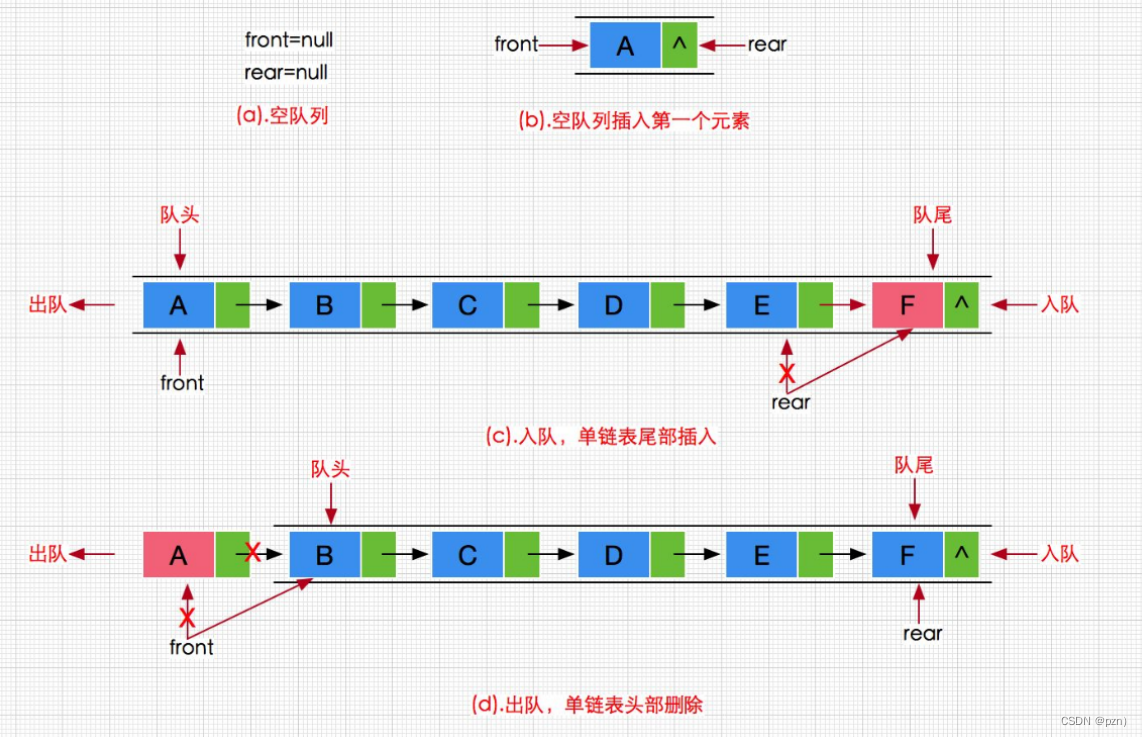
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out)入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
2.2队列的实现
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
#include"Queue.h"
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->phead;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
// 队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}newnode->next = NULL;newnode->val = x;if (pq->ptail == NULL){pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;}else{pq->ptail->next = newnode;pq->ptail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}// 队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->size != 0);//一个节点if (pq->phead->next == 0){free(pq->phead);pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;}//多个节点else{QNode* next = pq->phead->next;free(pq->phead);pq->phead = next;}pq->size--;
}// 取队头和队尾的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->phead);return pq->phead->val;
}QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->ptail);return pq->ptail->val;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size == 0;
}3.栈和队列经典题目
1.括号匹配问题
20. 有效的括号 - 力扣(LeetCode)

思路:(C语言)
利用已经实现好的栈
每个左括号要跟离自己最近的右括号匹配
左括号,入栈
右括号,取栈顶判断是否匹配
/*给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。有效字符串需满足:左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef char STDataType;typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->a = NULL;//top指向栈顶数据的下一个位置pst->top = 0;//top指向栈顶数据//pst->top = -1;pst->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}//入栈
void STpush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);//扩容if (pst->top == pst->capacity){int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;//三目操作符,如果pst->capacity等于0:赋4,不等于:扩容2倍STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->a = tmp;pst->capacity = newcapacity;}pst->a[pst->top] = x;pst->top++;
}//出栈
void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;//直接覆盖
}//取栈顶数据
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top == 0;
}//获取数据个数
int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}//每个左括号要跟离自己最近的右括号匹配
//左括号,入栈
//右括号,取栈顶判断是否匹配
bool isValid(char* s) {ST st;STInit(&st);while (*s){//左括号入栈if (*s == '(' || *s == '[' || *s == '{'){STpush(&st, *s);}else//右括号{if (STEmpty(&st))//判空{STDestroy(&st);//空,销毁,返回falsereturn false;}char top = STTop(&st);//取栈顶顶数据STPop(&st);//出栈//不匹配if ((top == '(' && *s != ')')|| (top == '{' && *s != '}')|| (top == '[' && *s != ']')){STDestroy(&st);return false;}}++s;}//栈不为空,说明左括号比右括号多,数量不匹配bool ret = STEmpty(&st);STDestroy(&st);return ret;
}2. 用队列实现栈

利用两个队列
把队尾前面全部数据给到另一个队列,就能取到队尾相当于栈顶的数据
typedef int QDataType;typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType val;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* phead;QNode* ptail;int size;
}Queue;void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);// 队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
// 队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);// 取队头和队尾的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->phead;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
// 队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}newnode->next = NULL;newnode->val = x;if (pq->ptail == NULL){pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;}else{pq->ptail->next = newnode;pq->ptail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}// 队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->size != 0);//一个节点if (pq->phead->next == 0){free(pq->phead);pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;}//多个节点else{QNode* next = pq->phead->next;free(pq->phead);pq->phead = next;}pq->size--;
}// 取队头和队尾的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->phead);return pq->phead->val;
}QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->ptail);return pq->ptail->val;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size == 0;
}
//利用两个队列
//把队尾前面全部数据给到另一个队列,就能取到队尾相当于栈顶的数据typedef struct {Queue q1;Queue q2;
} MyStack;//初始化
MyStack* myStackCreate() {MyStack* pst=(MyStack* )malloc(sizeof(MyStack));QueueInit(&(pst->q1));QueueInit(&(pst->q2));return pst;
}
//将元素 x 压入栈顶。
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {//两个队列哪个不为空就插入哪个if(!QueueEmpty( &(obj->q1) ) ){QueuePush(&(obj->q1),x);}else{QueuePush(&(obj->q2),x);}
}
//移除并返回栈顶元素。
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {//假设法Queue* empty=&(obj->q1);Queue* nonEmpty=&(obj->q2);if(!QueueEmpty(&(obj->q1))){empty=&(obj->q2);nonEmpty=&(obj->q1);}//不为空前size-1导走,删除最后一个就是栈顶数据while(QueueSize(nonEmpty)>1){QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(nonEmpty));QueuePop(nonEmpty);}int top=QueueFront(nonEmpty);QueuePop(nonEmpty);return top;
}
//返回栈顶元素
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {if(!QueueEmpty(&(obj->q1))){return QueueBack(&(obj->q1));//去队尾数据}else{return QueueBack(&(obj->q2));}
}
//如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {return QueueEmpty(&(obj->q1)) && QueueEmpty(&(obj->q2));
}
//销毁
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {QueueDestroy(&(obj->q1));QueueDestroy(&(obj->q2));free(obj);
}
感谢观看




