146. LRU 缓存
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现
LRUCache类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。函数
get和put必须以O(1)的平均时间复杂度运行。示例:
输入 ["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"] [[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]] 输出 [null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]解释 LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2); lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1} lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2} lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1 lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3} lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到) lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3} lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到) lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3 lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4提示:
1 <= capacity <= 30000 <= key <= 100000 <= value <= 105- 最多调用
2 * 105次get和put
解法1:Map + ArrayList (key)
用一个Map来存放key和value,一个ArrayList来存放访问顺序。
当用户get、put的key存在时,则从ArrayList中找到对应的key删除,然后把新访问的key放到尾部。
头部表示最久未访问的数据,尾部表示最新访问的数据。与数据结构匹配。
class LRUCache {private int capacity;private Map<Integer,Integer> cache;private List<Integer> delete;public LRUCache(int capacity) {this.cache = new HashMap<>(capacity);this.capacity = capacity;this.delete = new ArrayList<>(capacity);}public int get(int key) {Integer value = cache.get(key);if(value != null){// update to delete queuedelete.remove((Integer)key);delete.add((Integer)key);return value;}return -1;}public void put(int key, int value) {// if existedif (cache.containsKey(key)) {// update to delete queuedelete.remove((Integer)key);delete.add((Integer)key);cache.put(key, value);return;}// if cache is full, need to deleteif(cache.size() == capacity){Integer deleteKey = delete.remove(0);cache.remove(deleteKey);}cache.put(key, value);delete.add(key);}}/*** Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);* int param_1 = obj.get(key);* obj.put(key,value);*/ 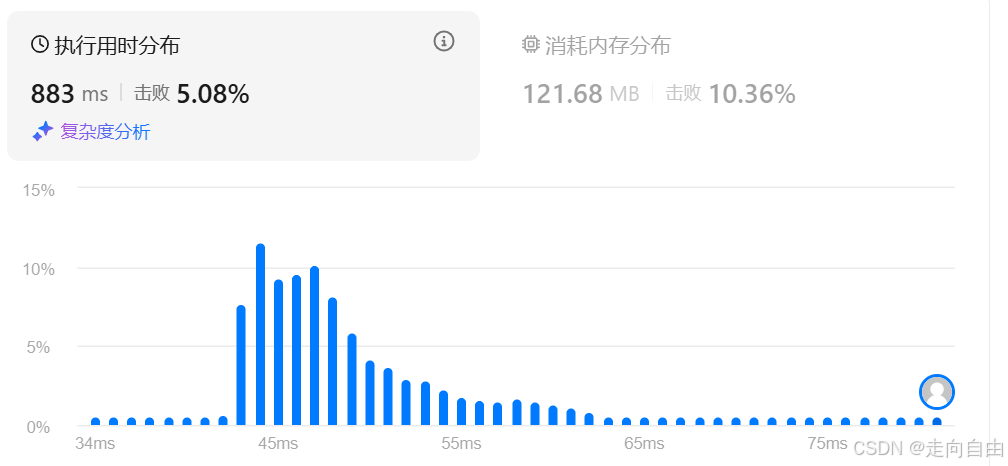
性能不怎么好,花了883ms。大部分时间花在ArrayList中查找key的位置和删除key后移动元素上了。
那我们想办法改进下,查找和删除。
解法2:Map + ArrayList (key, timestamp)
我们看到解法1中大部分时间都是在ArrayList中查找key和删除后移动数据。那么我们能不能不移动数据?答案是可以的。
方法是:我们每次操作key后为其引入一个timestamp,需要删除这个key时,比较待删除的timestamp是否没有更新过,没更新过则删除。这里使用程序启动后的纳秒,防止在同一个微秒内完成了多个操作,不能区分。
class LRUCache {private int capacity;private Map<Integer,KeyTime> cache;private List<KeyTime> delete;public LRUCache(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;this.cache = new HashMap<>(capacity*3/2);this.delete = new LinkedList<>();}public int get(int key) {KeyTime kt = cache.get(key);if(kt != null){long time = System.nanoTime();kt.time = time;// update to delete queuedelete.add(new KeyTime(key, kt.value, time));return kt.value;}return -1;}public void put(int key, int value) {long time = System.nanoTime();// if existedKeyTime kt = cache.get(key);if (kt != null) {kt.time = time;kt.value = value;// update to delete queuedelete.add(new KeyTime(key, value, time));return;}// if cache is full, need to deleteif(cache.size() == capacity){while(true) {KeyTime deleteKt = delete.remove(0);KeyTime existKt = cache.get(deleteKt.key);if (existKt != null && existKt.time == deleteKt.time) {cache.remove(deleteKt.key);break;}}}cache.put(key, new KeyTime(key, value, time));delete.add(new KeyTime(key, value, time));}static class KeyTime {int key;int value;long time;public KeyTime(int key, int value, long time) {this.key = key;this.value = value;this.time = time;}}}/*** Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);* int param_1 = obj.get(key);* obj.put(key,value);*/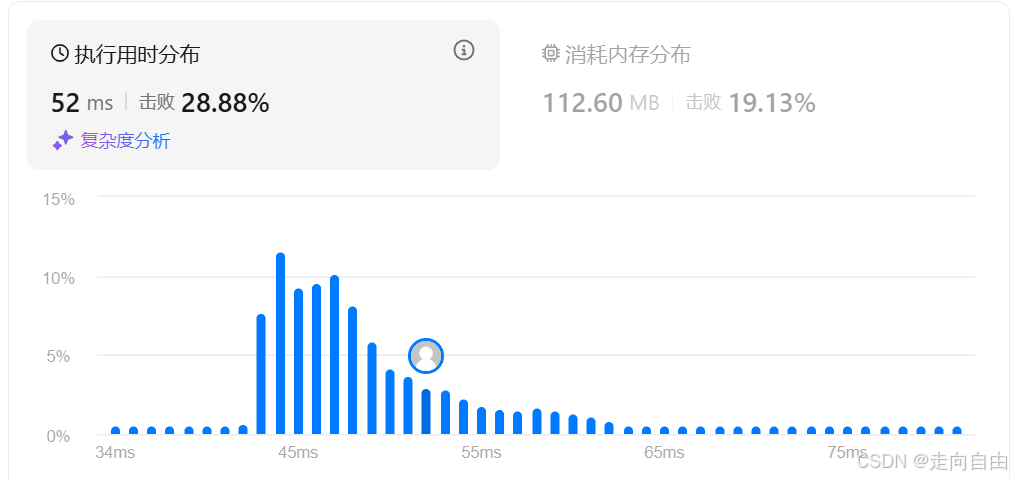
性能已经从883ms提升到了52ms,历史性的飞跃。还不错,可惜才28.88%,要是还想进一步优化的话,可以参考官方的LinkedHashMap实现。
解法3:HashMap + 双向链表 = LinkedHashMap
这里get/put 后把新访问的节点移动到表尾处,表头存放的是最久未访问的数据。
具体实现如下:
public class LRUCache {/*** use double direction linked list to store the order which to evict over due key.*/private int capacity;private Map<Integer,Node> cache;// store the first node to delete which is unused for a long timeprivate Node head;// store the used node recentlyprivate Node tail;public LRUCache(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;this.cache = new HashMap<>(capacity);this.head = new Node(-1, 0, null, null);this.tail = new Node(-2, 0, head, null);this.head.next = tail;}public int get(int key) {Node node = cache.get(key);if (node != null) {// existed then move to headmoveToTail(node);return node.value;}return -1;}public void put(int key, int value) {Node node = cache.get(key);if (node != null) {// existed, only need to update positionmoveToTail(node);node.value = value;return;}// cache is full, get the last unused node to removeif (cache.size() == capacity) {// remove the head node which is unused for a long timeNode toDelete = head.next;deleteNode(toDelete);cache.remove(toDelete.key);}node = new Node(key, value, null, null);cache.put(key, node);addToTail(node);}static class Node {int key;int value;Node previous;Node next;public Node(int key, int value, Node previous, Node next) {this.key = key;this.value = value;this.previous = previous;this.next = next;}}public void moveToTail(Node node) {deleteNode(node);addToTail(node);}/*** delete node from list.*/public void deleteNode(Node node) {node.previous.next = node.next;node.next.previous = node.previous;}/*** add node to list tail.*/public void addToTail(Node node) {node.next = tail;node.previous = tail.previous;tail.previous.next = node;tail.previous = node;}
}
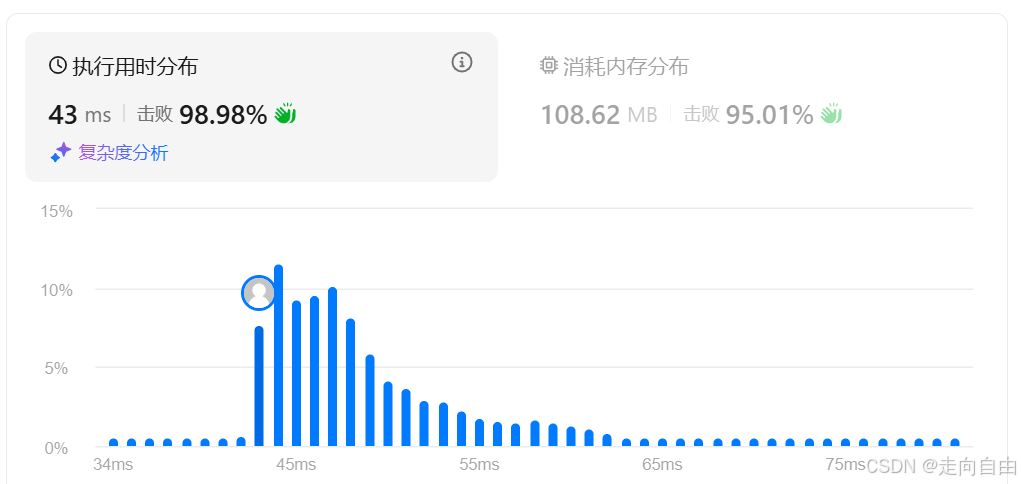
运行时间43ms,超越98.98%,可以了。




