一、顺序表
1.1顺序表的概念及结构
1.2静态顺序表
静态顺序表,即使用定长的数组来存储元素,用下面一张图就可以清楚看懂

1.3 动态顺序表
动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。 与静态顺序表不同,动态顺序表使用的数组大小可以动态变化,从而实现更灵活的储存数据。
二、动态顺序表的实现
2.1 顺序表的初始化
// 顺序表初始化
void SeqListInit(SeqList* psl)
{assert(psl);psl->array = (SLDataType*)malloc(sizeof(SLDataType) * 4);if (psl->array == NULL){perror("malloc failed");exit(-1);}psl->capacity = 4;psl->size = 0;
}2.2 顺序表的扩容
// 检查空间,如果满了,进行增容
void CheckCapacity(SeqList* psl)
{if (psl->capacity == psl->size){SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(psl->array, sizeof(SLDataType) * psl->capacity * 2);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc failed");exit(-1);}psl->array = tmp;psl->capacity *= 2;}else{return;}
}2.3顺序表的头插和尾插
头插:
// 顺序表头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
{assert(psl);CheckCapacity(psl);int i = 0;for (i = psl->size; i > 0; i--){psl->array[i] = psl->array[i - 1];}psl->array[0] = x;psl->size++;
}尾插:
// 顺序表尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
{assert(psl);CheckCapacity(psl);psl->array[psl->size] = x;psl->size++;
}2.4顺序表的头删和尾删
头删:
// 顺序表头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* psl)
{assert(psl);if (psl->size == 0){return;}else{int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < psl->size - 1; i++){psl->array[i] = psl->array[i + 1];}psl->size--;}
}尾删:
// 顺序表尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* psl)
{assert(psl);if (psl->size == 0){return;}else{psl->size--;}
}2.5顺序表的查找
// 顺序表查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
{assert(psl);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < psl->size - 1; i++){if (psl->array[i] == x){return i;}}return -1;
}2.6顺序表的打印和销毁
打印:
// 顺序表打印
void SeqListPrint(SeqList* psl)
{int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < psl->size - 1; i++){printf("%d ",psl->array[i]);}printf("\n");
}销毁:
// 顺序表销毁
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* psl)
{free(psl->array);psl->array = NULL;psl->capacity = 0;psl->size = 0;
}三、顺序表总代码
typedef int SLDataType;
// 顺序表的动态存储
typedef struct SeqList
{SLDataType* array;int size;int capacity;
}SeqList;// 基本增删查改接口
// 顺序表初始化
void SeqListInit(SeqList* psl)
{assert(psl);psl->array = (SLDataType*)malloc(sizeof(SLDataType) * 4);if (psl->array == NULL){perror("malloc failed");exit(-1);}psl->capacity = 4;psl->size = 0;
}
// 检查空间,如果满了,进行增容
void CheckCapacity(SeqList* psl)
{if (psl->capacity == psl->size){SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(psl->array, sizeof(SLDataType) * psl->capacity * 2);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc failed");exit(-1);}psl->array = tmp;psl->capacity *= 2;}else{return;}
}
// 顺序表尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
{assert(psl);CheckCapacity(psl);psl->array[psl->size] = x;psl->size++;
}
// 顺序表尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* psl)
{assert(psl);if (psl->size == 0){return;}else{psl->size--;}
}
// 顺序表头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
{assert(psl);CheckCapacity(psl);int i = 0;for (i = psl->size; i > 0; i--){psl->array[i] = psl->array[i - 1];}psl->array[0] = x;psl->size++;
}
// 顺序表头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* psl)
{assert(psl);if (psl->size == 0){return;}else{int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < psl->size - 1; i++){psl->array[i] = psl->array[i + 1];}psl->size--;}
}
// 顺序表查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x)
{assert(psl);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < psl->size - 1; i++){if (psl->array[i] == x){return i;}}return -1;
}// 顺序表销毁
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* psl)
{free(psl->array);psl->array = NULL;psl->capacity = 0;psl->size = 0;
}
// 顺序表打印
void SeqListPrint(SeqList* psl)
{int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < psl->size - 1; i++){printf("%d ",psl->array[i]);}printf("\n");
}
int main()
{SeqList list;SeqListInit(&list);SeqListPushBack(&list, 1);SeqListPushBack(&list, 2);SeqListPushBack(&list, 3);SeqListPushBack(&list, 4);SeqListPrint(&list);SeqListPopBack(&list);SeqListPrint(&list);SeqListPushFront(&list, 0);SeqListPrint(&list);SeqListPopFront(&list);SeqListPrint(&list);return 0;
}四、栈
4.1 栈的概念
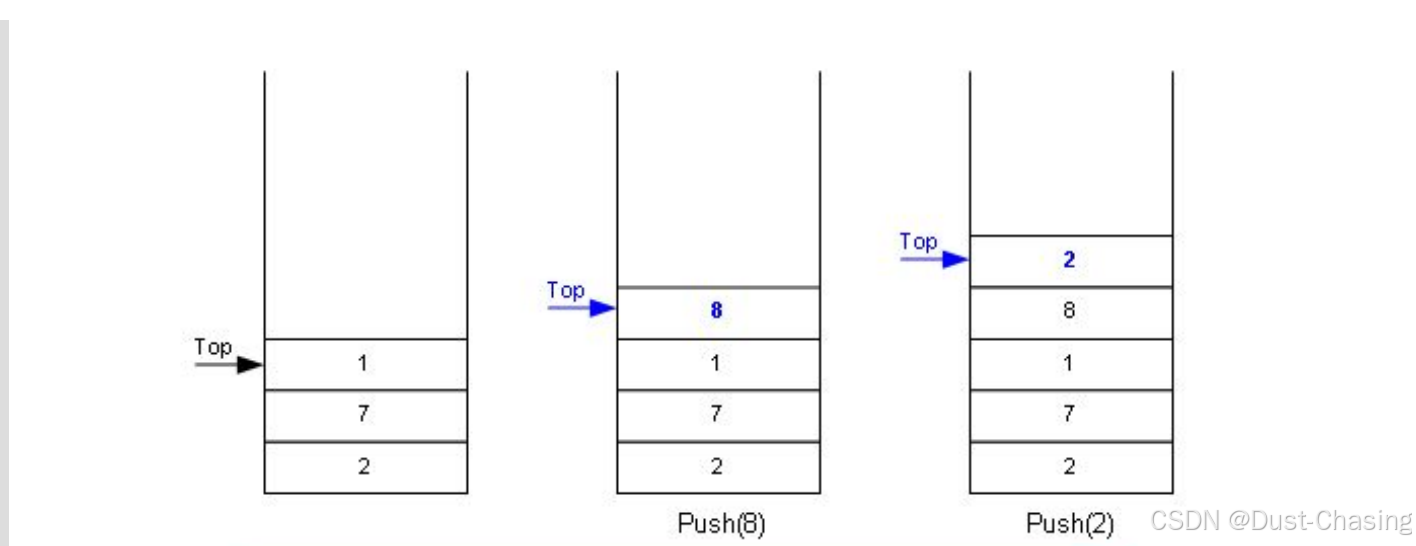
在讲完顺序表后,我们来继续看一种特殊的数据结构----栈, 为什么说它特殊,原因在于栈中的元素需要遵循一个后进先出原则(LIFO)。它一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。
进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
4.2 栈的实现
理论上来讲,栈既可以用链式结构实现即链表也可以用数组实现,但是由于栈的数据都是在元素末尾操作的特殊性,我们这里选择数组来实现更为方便 。(之所以与顺序表写在一起是因为这两个数据结构的结构很相似,我们也可以把栈看作一种特殊的顺序表)
栈的初始化:
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);if (ps->a == NULL){perror("malloc failed");exit(-1);}ps->capacity = 4;ps->top = 0; // 下一个元素插入的位置
}入栈/压栈:
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{if (ps->capacity == ps->top){STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * ps->capacity * 2);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc failed");exit(-1);}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity *= 2;}ps->a[ps->top] = data;ps->top++;
}出栈:
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == 0){return;}ps->top--;
}获取栈顶元素:
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top - 1 > 0);return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}栈中有效元素个数:
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}检测栈是否为空,不为空则返回0:
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}销毁栈:
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = 0;ps->top = 0;
}4.3 栈总代码
// 支持动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top; // 栈顶int capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);if (ps->a == NULL){perror("malloc failed");exit(-1);}ps->capacity = 4;ps->top = 0; // 下一个元素插入的位置
}
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{if (ps->capacity == ps->top){STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * ps->capacity * 2);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc failed");exit(-1);}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity *= 2;}ps->a[ps->top] = data;ps->top++;
}
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == 0){return;}ps->top--;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top - 1 > 0);return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = 0;ps->top = 0;
}
int main()
{Stack stack;StackInit(&stack);// 测试入栈StackPush(&stack, 1);StackPush(&stack, 2);StackPush(&stack, 3);StackPush(&stack, 4);// 测试栈顶元素printf("栈顶元素: %d\n", StackTop(&stack)); // 应该输出4// 测试出栈StackPop(&stack);printf("栈顶元素: %d\n", StackTop(&stack)); // 应该输出3// 测试栈的大小printf("栈的大小: %d\n", StackSize(&stack)); // 应该输出3// 测试栈是否为空printf("栈是否为空: %d\n", StackEmpty(&stack)); // 应该输出0(false)// 清空栈while (!StackEmpty(&stack)){printf("弹出元素: %d\n", StackTop(&stack));StackPop(&stack);}// 测试栈是否为空printf("栈是否为空: %d\n", StackEmpty(&stack)); // 应该输出1(true)// 销毁栈StackDestroy(&stack);return 0;
}



