一、实验目的
1、了解文件系统功能及实现原理。
2、掌握LINUX下文件操作的有关系统调用。
3、熟悉main函数带参数运行的有关操作过程。
4、通过模拟程序实现简单的一级文件系统或二级文件系统。
二、实验内容
1、编程显示文件自身。(1分)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
void main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int p;
char ch;
if(argc!=2)
{
printf("you forget to enter a filename\n");
exit(0);
}
if((p=open(argv[1],O_RDONLY))==-1) //以只读方式打开文件
{
printf("File open failare\n");
exit(0);
}
while(read(p,&ch,1)==1) //每次读一个字符到ch
printf("%c",ch);
close(p); //关闭文件
}
运行结果截屏:(包含编译、运行命令)

- 编程实现文件加密和解密(要求用系统功能调用实现文件的打开以及读写操作,并用main函数带参数方式编写程序)。(4分)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define SHIFT 3 // 加密和解密移位数
// 加密函数
void encrypt(FILE *file) {
rewind(file); // 回到文件开始位置
int ch;
while ((ch = fgetc(file)) != EOF) {
// 对字母进行加密
if (isalpha(ch)) {
char base = islower(ch) ? 'a' : 'A';
ch = (ch - base + SHIFT) % 26 + base;
fseek(file, -1, SEEK_CUR); // 回到当前字符的位置
fputc(ch, file); // 写入加密后的字符
}
}
fflush(file); // 确保所有缓冲的数据都写入文件
}
// 解密函数
void decrypt(FILE *file) {
rewind(file); // 回到文件开始位置
int ch;
while ((ch = fgetc(file)) != EOF) {
// 对字母进行解密
if (isalpha(ch)) {
char base = islower(ch) ? 'a' : 'A';
ch = (ch - base - SHIFT + 26) % 26 + base;
fseek(file, -1, SEEK_CUR); // 回到当前字符的位置
fputc(ch, file); // 写入解密后的字符
}
}
fflush(file); // 确保所有缓冲的数据都写入文件
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc != 3) {
printf("Usage: %s <encrypt/decrypt> <filename>\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
FILE *file = fopen(argv[2], "r+");
if (file == NULL) {
perror("Error opening file");
return 1;
}
// 根据命令行参数决定执行加密还是解密
if (strcmp(argv[1], "encrypt") == 0) {
encrypt(file);
} else if (strcmp(argv[1], "decrypt") == 0) {
decrypt(file);
} else {
printf("Invalid operation. Use 'encrypt' or 'decrypt'.\n");
fclose(file);
return 1;
}
fclose(file);
return 0;
}
运行结果截屏:(包含编译、运行命令)
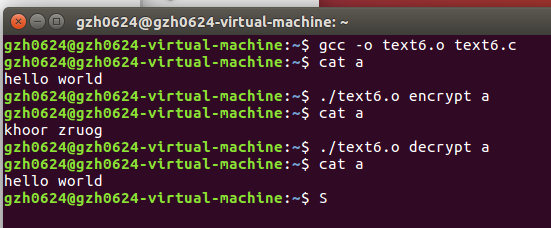
- 编程实现文件的合并。(要求用系统功能调用实现文件的打开及操作,并用main 函数带参数形式编写程序)
1)以写方式打开file1,以读方式打开file2文件,利用lseek()将file1的指针定位到文件尾部,再将file2写入到file1,实现文件合并。(1分)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
// 函数声明
void displayError(char *message);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
// 检查命令行参数的数量
if (argc != 3) {
printf("Usage: %s <destination_file> <source_file>\n", argv[0]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 打开目标文件,以便写入
int destFileDescriptor = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
if (destFileDescriptor == -1) {
displayError("Error opening destination file");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 打开源文件,以便读取
int srcFileDescriptor = open(argv[2], O_RDONLY);
if (srcFileDescriptor == -1) {
displayError("Error opening source file");
close(destFileDescriptor);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 读取源文件内容并写入目标文件
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
ssize_t bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = read(srcFileDescriptor, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE)) > 0) {
if (write(destFileDescriptor, buffer, bytesRead) != bytesRead) {
displayError("Error writing to destination file");
close(destFileDescriptor);
close(srcFileDescriptor);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
}
// 检查读取源文件时是否发生错误
if (bytesRead == -1) {
displayError("Error reading source file");
close(destFileDescriptor);
close(srcFileDescriptor);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 关闭文件描述符
close(destFileDescriptor);
close(srcFileDescriptor);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
// 显示错误信息的函数
void displayError(char *message) {
perror(message);
}
运行结果截屏:(包含编译、运行命令)

- 以读方式打开file1、file2文件,以写方式打开file3文件,实现文件合并。(1分)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
// 函数声明
void displayError(char *message);
int copyContent(int srcFileDescriptor, int destFileDescriptor);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
// 检查命令行参数的数量
if (argc != 4) {
printf("Usage: %s <source_file_a> <source_file_b> <destination_file_c>\n", argv[0]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 打开第一个源文件(a),以便读取
int fileADescriptor = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (fileADescriptor == -1) {
displayError("Error opening the source file a");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 打开第二个源文件(b),以便读取
int fileBDescriptor = open(argv[2], O_RDONLY);
if (fileBDescriptor == -1) {
displayError("Error opening the source file b");
close(fileADescriptor);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 打开目标文件(c),以便写入
int fileCDescriptor = open(argv[3], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
if (fileCDescriptor == -1) {
displayError("Error opening the destination file c");
close(fileADescriptor);
close(fileBDescriptor);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 复制第一个源文件(a)的内容到目标文件(c)
if (copyContent(fileADescriptor, fileCDescriptor) == -1) {
displayError("Error copying the source file a");
close(fileADescriptor);
close(fileBDescriptor);
close(fileCDescriptor);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 复制第二个源文件(b)的内容到目标文件(c)
if (copyContent(fileBDescriptor, fileCDescriptor) == -1) {
displayError("Error copying the source file b");
close(fileADescriptor);
close(fileBDescriptor);
close(fileCDescriptor);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fileADescriptor);
close(fileBDescriptor);
close(fileCDescriptor);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
// 复制文件内容的函数
int copyContent(int srcFileDescriptor, int destFileDescriptor) {
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
ssize_t bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = read(srcFileDescriptor, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE)) > 0) {
if (write(destFileDescriptor, buffer, bytesRead) != bytesRead) {
return -1;
}
}
if (bytesRead == -1) {
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
// 显示错误信息的函数
void displayError(char *message) {
perror(message);
}
运行结果截屏:(包含编译、运行命令)

3)以附加方式打开file1,以读方式打开file2,实现文件合并。(1分)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
// 函数声明
void displayError(char *message);
int copyContent(int srcFileDescriptor, int destFileDescriptor);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
// 检查命令行参数的数量
if (argc != 3) {
printf("Usage: %s <source_file_b> <destination_file_a>\n", argv[0]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 打开源文件(b),以便读取
int fileBDescriptor = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (fileBDescriptor == -1) {
displayError("Error opening the source file b");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 打开目标文件(a),以便附加内容
int fileADescriptor = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_APPEND);
if (fileADescriptor == -1) {
displayError("Error opening the destination file a");
close(fileBDescriptor);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 复制源文件(b)的内容到目标文件(a)的末尾
if (copyContent(fileBDescriptor, fileADescriptor) == -1) {
displayError("Error copying the source file b");
close(fileBDescriptor);
close(fileADescriptor);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fileBDescriptor);
close(fileADescriptor);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
// 复制文件内容的函数
int copyContent(int srcFileDescriptor, int destFileDescriptor) {
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
ssize_t bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = read(srcFileDescriptor, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE)) > 0) {
if (write(destFileDescriptor, buffer, bytesRead) != bytesRead) {
return -1;
}
}
if (bytesRead == -1) {
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
// 显示错误信息的函数
void displayError(char *message) {
perror(message);
}
运行结果截屏:(包含编译、运行命令)

- 编程实现一个简单的文件系统,要求实现以下功能:
文件创建 文件解密 文件显示 文件列目录 文件删除
文件加密 文件合并 文件查询 文件复制 文件重命名 (选做题)
注:
- 选做该题的同学,不用做前面的题,直接提交这一道题的程序和结果即可,成绩直接给优秀。
- 要求用系统功能调用实现文件的打开及操作。
- 要求列出程序编译、运行过程以及执行结果截屏。
- 结果截屏要求给出至少5个结果(比如,创建、加密、解密、合并、复制等)。
- 5、编程实现一个二级文件系统,要求给出设计分析并列出程序编译、运行过程以及执行结果的部分截屏。(附加题)
三、实验总结和体会(1分)
通过本次操作系统文件操作实验,我对文件的打开、读写操作以及加密解密的实现有了更深入的了解。
在实验中,我学会了如何使用系统函数来打开文件,并对文件进行读写操作。我了解到文件的打开模式可以根据需要选择读取、写入或者读写模式,并且可以指定以二进制模式还是文本模式打开文件。另外,我也了解到可以使用fopen、fclose、fread、fwrite等系统函数来进行文件的打开、关闭、读取和写入操作。
我还学会了如何使用异或运算符实现简单的文件加密和解密。通过将密钥与文件内容进行异或操作,可以实现简单的加密和解密功能。虽然这种加密方式并不安全,但它给我展示了加密算法的基本原理。
通过本次实验,我进一步巩固了C语言的基本语法和文件操作的相关知识。我也意识到文件操作在实际应用中的重要性,不仅可以帮助我们处理和管理文件,还可以用于实现文件的安全保护。
总的来说,本次实验让我更深入地了解了文件操作和加密解密的实现方法,并让我更加熟悉和掌握了C语言的相关知识。通过实践,我对操作系统文件操作有了更深入的理解,这对我今后的学习和工作都是非常有益的。




