引言
在学习过第一个springMVC项目建造过后,让我们直接进入真实开发中所必需的注解开发,
是何等的简洁高效!!
注:由于Maven可能存在资源过滤的问题,在maven依赖中加入
<build><resources><resource><directory>src/main/resources</directory><includes><include>**/*.properties</include><include>**/*.xml</include></includes><filtering>true</filtering></resource><resource><directory>src/main/java</directory><includes><include>**/*.properties</include><include>**/*.xml</include></includes><filtering>true</filtering></resource></resources></build>第一步:在pom.xml文件引入相关的依赖
主要有spring框架核心库。springmvc,servlet,JSTL(jsp标准标签库),已经在父依赖中了
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>junit</groupId><artifactId>junit</artifactId><version> 4.13.2</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId><version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId><version>4.0.1</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId><artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId><version>2.2</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>jstl</artifactId><version>1.2</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId><version>2.5</version></dependency></dependencies><build><resources><resource><directory>src/main/resources</directory><includes><include>**/*.properties</include><include>**/*.xml</include></includes><filtering>true</filtering></resource><resource><directory>src/main/java</directory><includes><include>**/*.properties</include><include>**/*.xml</include></includes><filtering>true</filtering></resource></resources></build>第二步:配置web.xml
注:
-
注册DispatcherServlet
-
关联sprigMVC的配置文件
-
启动级别为1
-
映射路径为/(不能为/*)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"version="4.0"><servlet><servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name><url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping>
</web-app>第三步:配置springmvc-servlet.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/mvchttp://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!--自动扫描包,让指定包下的注解生效,由IOC容器统一管理--><context:component-scan base-package="com.lyc.controller"/>
<!-- 资源过滤 让springMVC不处理静态资源 .css .js .html.mp3 --><mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
<!--
支持mvc注解驱动
在spring中一般采用@RequestMappering注解来完成映射关系
要想使@RequestMapping注解生效
必须要上下文中注册DefaultAnnotationHandlerMappering和一个AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter实例
这两个实例分别在类级别和方法级别处理
而annotation-driven配置帮助我们自动完成上述两个实例的注入
--><mvc:annotation-driven/><!-- 视图解析器:模板引擎Thymeleaf Freemarker...,可以更换,也可以自定义--><bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="internalResourceViewResolver"><!-- 前缀 --><property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/><!-- 后缀 --><property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/></bean>
</beans>这些在spring配置文件就不需要动了,不用改变,直接使用,而在正常开发中,我们只需要修改视图解析器即可
注:在视图解析器中我们把所有的视图都存放在/WEB-INF/目录下,这样可以保证试图安全,因为这个目录下的文件,客户端不能直接访问。
第四步:创建Controller
package com.lyc.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller@RequestMapping("/HelloController")public class HelloController {//封装数据//真是访问地:项目名/HelloController/hello@RequestMapping("/hello")public String Hello(Model model){//向模型中添加属性msg与值,可以在JSP页面中取出并渲染model.addAttribute("msg","HelloSpringMVC!");//web-inf/jsp/hello.jspreturn "hello";}}解析代码:@controller是为了让Spring IOC 容器初始化时自动扫描到
@RequestMapping是为了映射请求路径,这里因为类和方法上都有映射,所以访问时应该是/HelloController/hello
方法中声明Model类型的参数是为了把Action中的数据带到视图中
方法返回的是视图的名称hello,加上配置文件中得前后缀变成WEB-INF/jsp/hello.jsp
第五步:创建视图层 web/WEB-INF/jsp/hello.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>Title</title></head><body>${msg}</body></html>运行时报错:

Unsupported class file major version 61
经过查询发现是jdk版本过高,我用的是jdk17,将版本改到jdk11重启,将maven配置文件中的版本改为11即可
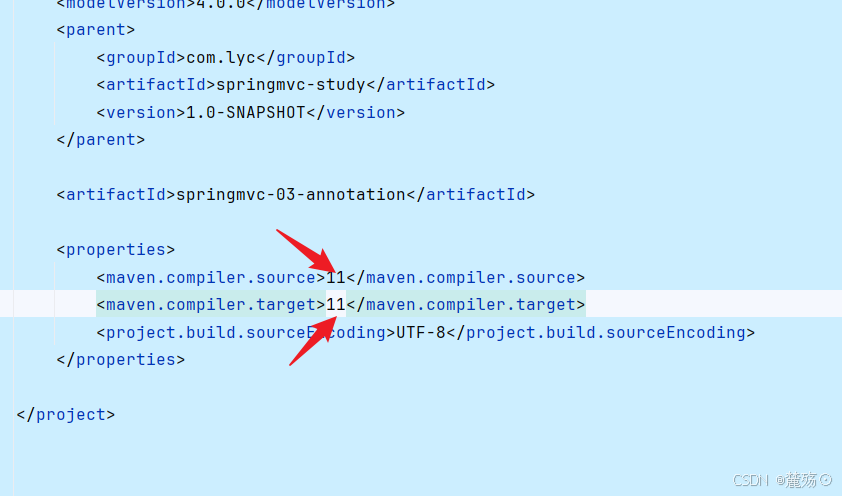
再次尝试运行
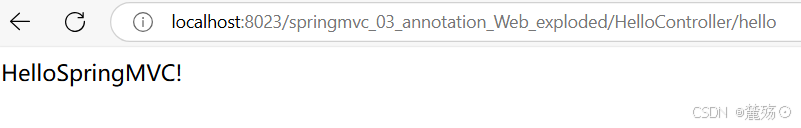
运行成功!
总结步骤:
-
新建maven项目
-
导入相关依赖
-
编写web.xml,注册DispatcherServlet
-
编写springmvc配置文件
-
创建对应的Controller类
-
完善前端视图和Controller之间的对应
-
测试运行测试
注:springMVC配置文件中的核心三要素:处理器映射器,处理器适配器,视图解析器,在注解开发的帮助下,我们只需要去手动配置视图解析器,而处理器映射器和处理器适配器只需要开启注解驱动即可< mvc:annotation-driven/> 是代码更加简洁高效!!!





