文章目录
- 摘要
- 安装包
- 安装timm
- 数据增强Cutout和Mixup
- EMA
- 项目结构
- 计算mean和std
- 生成数据集
摘要
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.19967
论文主要集中在介绍和分析一种新兴的学习范式——星操作(Star Operation),这是一种通过元素级乘法融合不同子空间特征的方法,通过元素级乘法(类似于“星”形符号的乘法操作)将不同子空间的特征进行融合,从而在多个研究领域中展现出出色的性能和效率。
星操作在自然语言处理(NLP)和计算机视觉(CV)等多个领域中都得到了成功应用。例如,在自然语言处理中,Monarch Mixer、Mamba、Hyena Hierarchy和GLU等模型都采用了星操作;在计算机视觉中,FocalNet、HorNet和VAN等模型也利用了星操作进行特征融合。
尽管星操作在多个领域中都取得了显著成果,但其背后的基本原理尚未得到全面分析和验证。StarNet通过深入探究星操作的细节,发现星操作具有将输入映射到极高维、非线性特征空间的能力。这种映射方式与传统增加网络宽度的方法不同,而是通过跨通道特征对乘实现了一种类似于多项式核函数的非线性高维映射。
当将星操作融入神经网络并堆叠多层时,每一层都使隐含的维度复杂度呈指数级增长。这种高效的特征融合方式使得星操作能够在紧凑的特征空间内实现近乎无限的维度,从而极大地提高了模型的表示能力和性能。
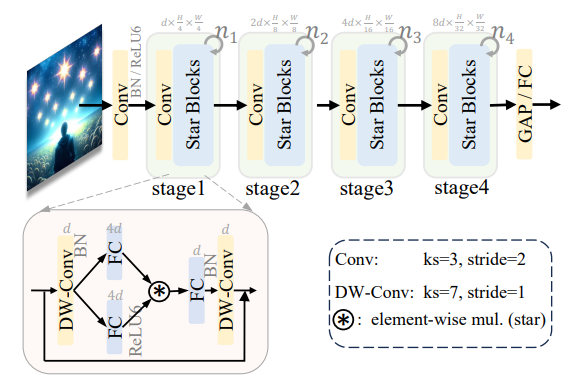
本文使用StarNet模型实现图像分类任务,模型选择starnet_s1,在植物幼苗分类任务ACC达到了95%+。


通过这篇文章能让你学到:
- 如何使用数据增强,包括transforms的增强、CutOut、MixUp、CutMix等增强手段?
- 如何实现StarNet模型实现训练?
- 如何使用pytorch自带混合精度?
- 如何使用梯度裁剪防止梯度爆炸?
- 如何使用DP多显卡训练?
- 如何绘制loss和acc曲线?
- 如何生成val的测评报告?
- 如何编写测试脚本测试测试集?
- 如何使用余弦退火策略调整学习率?
- 如何使用AverageMeter类统计ACC和loss等自定义变量?
- 如何理解和统计ACC1和ACC5?
- 如何使用EMA?
如果基础薄弱,对上面的这些功能难以理解可以看我的专栏:经典主干网络精讲与实战
这个专栏,从零开始时,一步一步的讲解这些,让大家更容易接受。
安装包
安装timm
使用pip就行,命令:
pip install timm
mixup增强和EMA用到了timm
数据增强Cutout和Mixup
为了提高成绩我在代码中加入Cutout和Mixup这两种增强方式。实现这两种增强需要安装torchtoolbox。安装命令:
pip install torchtoolbox
Cutout实现,在transforms中。
from torchtoolbox.transform import Cutout
# 数据预处理
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),Cutout(),transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5])])
需要导入包:from timm.data.mixup import Mixup,
定义Mixup,和SoftTargetCrossEntropy
mixup_fn = Mixup(mixup_alpha=0.8, cutmix_alpha=1.0, cutmix_minmax=None,prob=0.1, switch_prob=0.5, mode='batch',label_smoothing=0.1, num_classes=12)criterion_train = SoftTargetCrossEntropy()
Mixup 是一种在图像分类任务中常用的数据增强技术,它通过将两张图像以及其对应的标签进行线性组合来生成新的数据和标签。
参数详解:
mixup_alpha (float): mixup alpha 值,如果 > 0,则 mixup 处于活动状态。
cutmix_alpha (float):cutmix alpha 值,如果 > 0,cutmix 处于活动状态。
cutmix_minmax (List[float]):cutmix 最小/最大图像比率,cutmix 处于活动状态,如果不是 None,则使用这个 vs alpha。
如果设置了 cutmix_minmax 则cutmix_alpha 默认为1.0
prob (float): 每批次或元素应用 mixup 或 cutmix 的概率。
switch_prob (float): 当两者都处于活动状态时切换cutmix 和mixup 的概率 。
mode (str): 如何应用 mixup/cutmix 参数(每个’batch’,‘pair’(元素对),‘elem’(元素)。
correct_lam (bool): 当 cutmix bbox 被图像边框剪裁时应用。 lambda 校正
label_smoothing (float):将标签平滑应用于混合目标张量。
num_classes (int): 目标的类数。
EMA
EMA(Exponential Moving Average)是指数移动平均值。在深度学习中的做法是保存历史的一份参数,在一定训练阶段后,拿历史的参数给目前学习的参数做一次平滑。具体实现如下:
import logging
from collections import OrderedDict
from copy import deepcopy
import torch
import torch.nn as nn_logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)class ModelEma:def __init__(self, model, decay=0.9999, device='', resume=''):# make a copy of the model for accumulating moving average of weightsself.ema = deepcopy(model)self.ema.eval()self.decay = decayself.device = device # perform ema on different device from model if setif device:self.ema.to(device=device)self.ema_has_module = hasattr(self.ema, 'module')if resume:self._load_checkpoint(resume)for p in self.ema.parameters():p.requires_grad_(False)def _load_checkpoint(self, checkpoint_path):checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_path, map_location='cpu')assert isinstance(checkpoint, dict)if 'state_dict_ema' in checkpoint:new_state_dict = OrderedDict()for k, v in checkpoint['state_dict_ema'].items():# ema model may have been wrapped by DataParallel, and need module prefixif self.ema_has_module:name = 'module.' + k if not k.startswith('module') else kelse:name = knew_state_dict[name] = vself.ema.load_state_dict(new_state_dict)_logger.info("Loaded state_dict_ema")else:_logger.warning("Failed to find state_dict_ema, starting from loaded model weights")def update(self, model):# correct a mismatch in state dict keysneeds_module = hasattr(model, 'module') and not self.ema_has_modulewith torch.no_grad():msd = model.state_dict()for k, ema_v in self.ema.state_dict().items():if needs_module:k = 'module.' + kmodel_v = msd[k].detach()if self.device:model_v = model_v.to(device=self.device)ema_v.copy_(ema_v * self.decay + (1. - self.decay) * model_v)加入到模型中。
#初始化
if use_ema:model_ema = ModelEma(model_ft,decay=model_ema_decay,device='cpu',resume=resume)# 训练过程中,更新完参数后,同步update shadow weights
def train():optimizer.step()if model_ema is not None:model_ema.update(model)# 将model_ema传入验证函数中
val(model_ema.ema, DEVICE, test_loader)
针对没有预训练的模型,容易出现EMA不上分的情况,这点大家要注意啊!
项目结构
StarNet_Demo
├─data1
│ ├─Black-grass
│ ├─Charlock
│ ├─Cleavers
│ ├─Common Chickweed
│ ├─Common wheat
│ ├─Fat Hen
│ ├─Loose Silky-bent
│ ├─Maize
│ ├─Scentless Mayweed
│ ├─Shepherds Purse
│ ├─Small-flowered Cranesbill
│ └─Sugar beet
├─models
│ └─starnet.py
├─mean_std.py
├─makedata.py
├─train.py
└─test.py
mean_std.py:计算mean和std的值。
makedata.py:生成数据集。
train.py:训练StarNet模型
models:来源官方代码。
计算mean和std
为了使模型更加快速的收敛,我们需要计算出mean和std的值,新建mean_std.py,插入代码:
from torchvision.datasets import ImageFolder
import torch
from torchvision import transformsdef get_mean_and_std(train_data):train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=1, shuffle=False, num_workers=0,pin_memory=True)mean = torch.zeros(3)std = torch.zeros(3)for X, _ in train_loader:for d in range(3):mean[d] += X[:, d, :, :].mean()std[d] += X[:, d, :, :].std()mean.div_(len(train_data))std.div_(len(train_data))return list(mean.numpy()), list(std.numpy())if __name__ == '__main__':train_dataset = ImageFolder(root=r'data1', transform=transforms.ToTensor())print(get_mean_and_std(train_dataset))
数据集结构:
运行结果:
([0.3281186, 0.28937867, 0.20702125], [0.09407319, 0.09732835, 0.106712654])
把这个结果记录下来,后面要用!
生成数据集
我们整理还的图像分类的数据集结构是这样的
data
├─Black-grass
├─Charlock
├─Cleavers
├─Common Chickweed
├─Common wheat
├─Fat Hen
├─Loose Silky-bent
├─Maize
├─Scentless Mayweed
├─Shepherds Purse
├─Small-flowered Cranesbill
└─Sugar beet
pytorch和keras默认加载方式是ImageNet数据集格式,格式是
├─data
│ ├─val
│ │ ├─Black-grass
│ │ ├─Charlock
│ │ ├─Cleavers
│ │ ├─Common Chickweed
│ │ ├─Common wheat
│ │ ├─Fat Hen
│ │ ├─Loose Silky-bent
│ │ ├─Maize
│ │ ├─Scentless Mayweed
│ │ ├─Shepherds Purse
│ │ ├─Small-flowered Cranesbill
│ │ └─Sugar beet
│ └─train
│ ├─Black-grass
│ ├─Charlock
│ ├─Cleavers
│ ├─Common Chickweed
│ ├─Common wheat
│ ├─Fat Hen
│ ├─Loose Silky-bent
│ ├─Maize
│ ├─Scentless Mayweed
│ ├─Shepherds Purse
│ ├─Small-flowered Cranesbill
│ └─Sugar beet
新增格式转化脚本makedata.py,插入代码:
import glob
import os
import shutilimage_list=glob.glob('data1/*/*.png')
print(image_list)
file_dir='data'
if os.path.exists(file_dir):print('true')#os.rmdir(file_dir)shutil.rmtree(file_dir)#删除再建立os.makedirs(file_dir)
else:os.makedirs(file_dir)from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
trainval_files, val_files = train_test_split(image_list, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
train_dir='train'
val_dir='val'
train_root=os.path.join(file_dir,train_dir)
val_root=os.path.join(file_dir,val_dir)
for file in trainval_files:file_class=file.replace("\\","/").split('/')[-2]file_name=file.replace("\\","/").split('/')[-1]file_class=os.path.join(train_root,file_class)if not os.path.isdir(file_class):os.makedirs(file_class)shutil.copy(file, file_class + '/' + file_name)for file in val_files:file_class=file.replace("\\","/").split('/')[-2]file_name=file.replace("\\","/").split('/')[-1]file_class=os.path.join(val_root,file_class)if not os.path.isdir(file_class):os.makedirs(file_class)shutil.copy(file, file_class + '/' + file_name)
完成上面的内容就可以开启训练和测试了。





)